The coefficient in question is a technical value. The fact is that to measure the energy consumed by such a large object as an apartment building, special devices are used that reduce (transform) the load currents before feeding them into the common building meter. House-wide electricity meters, as a rule, are not connected directly to the house electrical network, since the consumer has a large consumption power, which cannot be connected through a regular direct connection meter. Direct connection electricity meters operate with low load currents. But since the household consumption currents are an order of magnitude higher, in order to prevent the meter from burning out, they must be reduced. This is done using current transformers; they are selected according to the consumer load. Thus, the transformation ratio varies depending on the equipment installed in the house. A meter connected through such a transformer does not record the actual energy consumed, but the energy reduced by the current transformer by 20, 40 or 60 times. This is the transformation coefficient.
To obtain real consumption, you need to multiply the meter readings by this coefficient. For example, if the meter showed a consumption of 70 kWh. and a transformer is used that reduces the load current by 20 times (transformation ratio is 20), then the real consumption (consumption) according to the ODPU will be 20 * 70 = 1,400 kW * h. This flow rate is included in the calculations of electricity for one-unit heating system.
In large buildings and facilities, special electricity control mechanisms are installed, which are designed for volumetric current indicators (over 100A). Therefore, there is a need to install step-down transformers. To correctly take readings from all devices, you need a calculated electricity metering factor.
What is transformation ratio
The transformation ratio of an electricity meter is a technical parameter that determines the accuracy of readings from energy consumption metering devices.
Electricity meters of large facilities (industrial, commercial, etc.) are not connected directly to the general building network, because classic devices do not provide the required voltage level. To reduce the likelihood of breakdown, it is necessary to reduce the input power data through the installed transformers.
The calculated electricity metering coefficient is an indicator that reflects the ratio of current strength and meter data. If the amount of electricity consumed is large, the devices do not reflect the actual amount, so an additional calculation is used. The coefficient figure is several points higher than one. When multiplied, the value of the actual consumed electricity is obtained.
Another point is the transformer level in terms of error. Energy meters correspond to 0.5 or 0.2. The higher the value, the less accurate the devices show.
Induction models
This type of measuring instrument is the most common.
Its design includes two metal coils; the magnetic field created by the current sets them in motion, as a result of which the disk equipped with a scale rotates.
The operating speed of the device is directly dependent on the voltage, so with reduced electricity consumption it will spin more slowly.
More on the topic How much does MTPL car insurance cost for a novice driver without experience?
The disadvantage of these meters is their significant measurement error; they can last about 15 years, which is a good indicator.
Devices of the first type have two coils, one of them limits the alternating current, eliminating inaccuracies and forming a magnetic field. The second one generates alternating current. The advantages of these meters include their high performance and simple design. Despite voltage fluctuations, such meters will last a very long time.
Formula for determining CT
Calculation of electric meter readings with current transformers and corresponding coefficients is carried out according to a certain formula. The result reflects the required scaling - up or down the data. In other words, the transformer changes the voltage level and shows the fluctuations in numbers.
To understand how to correctly read an electricity meter with current transformers, it is worth understanding the formula used. In most cases, the transformation coefficient is encrypted with the English letters k and n (other characters are less common). If the designation on the transformer is k ˂ 1, then the device operates in a step-up mode, if k ˃ 1 – in a step-down mode.
Types of electricity metering devices
Electricity metering devices are multifunctional mechanisms that can reflect the current position of data, store and transmit important information. Today, three different types of counting mechanisms are used.
Mechanical or induction meters
The classic type of device that is most common. The design consists of two conventional coils. One of them limits the AC voltage data, preventing distortion and receiving electric current. The second converts the flow of alternating voltage.
The main advantages are ease of operation and durability of the devices. The service life of meters of this type is long, and the cost is low. The downside is the dimensions of the mechanism.
Mechanical devices have a large error, which is very noticeable when used in networks with low voltage.
Electronic meters
The devices have a higher level of accuracy in calculations, but their price is higher. An additional plus is the ability to operate in several modes (for example, morning and night, two- and three-tariff devices).
Electronic meters convert incoming analog readings into special digital encoding, which in turn are converted by a small microcontroller. The received data can be seen on the display. They are trying to install such devices more and more often, replacing outdated mechanical models.
Other advantages are compact size and the possibility of remote control.
Hybrid meters
They are a middle option between electronic and mechanical counters. On the one hand, devices are equipped with a digital display for convenience. On the other hand, they use the classic inductive method of obtaining and processing data.
Hybrid devices are rarely installed, preferring analog or electronic mechanisms.
Electronic meters
The accuracy class is indicated on the front side of the meter. The accuracy class of an electric meter is the maximum measurement error, which is indicated as a percentage.
According to current legislation, old electricity meters that belong to class 2.5 or more need to be replaced; instead, devices with accuracy class 1 or 2 are installed, but this is not done in all houses. An error of less than 1% can only be achieved at industrial facilities.
Ultimately, choosing a more accurate meter can be beneficial for the consumer, as it will reduce the amount of your electricity bill. Even when the meter is installed at the expense of the energy company, you can refuse the standard meter and choose the appropriate model yourself; if it meets the standards, then it is required to be installed.
Specialist's note: inspection seals on meters must be renewed at least once every 2 years; for three-phase devices, the interval is one year.
These meters are quite expensive, but the price justifies the quality. These devices have a high accuracy class, which reduces reading errors to a minimum. These devices have a multi-tariff function. The principle of operation of such a counter is based on the fact that it transforms the signal into a digital code, which is then decrypted by a microcontroller.
More on the topic Coefficient by region OSAGO, calculation criteria and on what factors the cost depends, as well as a table of territorial coefficients.
Useful tips
Electricity meters allow you to see the amount of energy consumed in order to adequately assess consumption and calculate the final payment. Devices differ in accuracy class, power, and degree of permissible error. To obtain accurate data, readings are taken and actual consumption is calculated using a coefficient and a calculator.
For residential buildings in urban areas and villages, small devices are used - single-phase meters (for example, Mercury 230 ART-03 CN, manufactured in Moscow) or multi-tariff devices suitable for a network of 220 Volts or 120 Amperes.
It is important that every new device has a government inspection seal. Without this, the electricity meter readings will not be considered reliable and will not be accepted by regulatory authorities. You can choose a suitable counter and calculate actual indicators yourself or through controllers.
The electricity meter transformation ratio (CT) is one of the technical quantities that affects the accuracy of the meter readings.
The indicator is determined by the operating efficiency of the transformer substation.
Let's analyze this value in detail.
Electronic meters
The accuracy of the electric meter readings also depends on the transformation ratio; this indicator is determined not based on the characteristics of the measuring device itself, but depends on the operating efficiency of the transformer substation.
To reduce energy losses, electricity is transported through high-voltage lines; voltage-reducing transformers are used to bring the network characteristics into line with the parameters of household appliances.
Thus, the home electricity meter does not record actual consumption, but only the amount of electricity with reduced voltage, so to determine the exact costs it is necessary to multiply the readings of the meter by the transformation ratio. Correspondence between the transformation ratio and the rated voltage Many utility companies do this in advance, when drawing up tariffs for the population, in this case the average value is used.
You might be interested in an article about
benefits for electricity payments
.
Read an article on how to check your electricity meter at home here.
What is transformation ratio?
Such electric meters do not have a direct connection to the home’s electrical network, which is due to the inability to connect high voltage using traditional direct-connection devices.
Thus, in order to prevent damage to meters, it is necessary to reduce the power ratings for the supplied voltage using transformer standard equipment. The choice of such equipment is directly influenced by the level of required load.
The transformation coefficient of electrical energy metering devices may vary depending on the characteristics of the installed equipment. As a result, meters for measuring electricity costs, operating with transformers, record the load, which is reduced by several tens of times.
The concept of transformation ratio
To carry out rational control of electricity at large facilities, special equipment is used that reduces the power at the output of the electric meter.
These devices are not directly connected to the building's electrical network, which means that it is impossible to directly connect high-voltage voltage to the general electrical network. It follows that in order to minimize the occurrence of malfunctions, it is necessary to reduce the power using transformer equipment. In this case, electricity meters will record a load reduced tens of times. The results obtained in this way will be CT, and in order to determine the real electricity consumption, you should multiply the electric meter readings by the calculated coefficient used.
How to determine the transformation ratio: formula

For indicators exceeding one, a decrease is made, and, conversely, for indicators less than one, a device of an increasing type is used.
Transformation ratios for voltage or current differ.
- U1 and U2 – difference in electrical voltage on the primary and secondary windings;
- N1 and N2 – number of turns of the primary and secondary windings;
- I2 and I1 – indicators of current strength in the primary and secondary windings;
- k – required CT parameters.
As a rule, such parameters of the transformation ratio are necessarily indicated in the accompanying documentation that comes with the equipment. You can also find out this information from the markings on the body of such a device.
A difficult situation is when the CT needs to be calculated independently, according to data obtained empirically. In this case, current is passed through the primary winding of the equipment and a short circuit is made on the secondary winding, after which the amount of electric current passing through the secondary winding is measured.
Types of electricity metering devices
Meters are multifunctional devices for recording consumption, as well as storing information on electrical energy consumption. Today, three versions of metering devices are in use, designed to account for consumed electrical energy. These include induction, electronic and hybrid models. The last option is the least common.
Mechanical or induction metering devices

Devices of this type consist of two coils.
The first voltage coil limits the parameters of alternating current, blocking interference and forming, in accordance with the voltage, a special magnetic flux.
The second current coil produces an alternating current.
The advantages of mechanical models include high reliability and structural simplicity, long service life, independence from voltage surges and affordable cost. When choosing induction devices, you need to take into account the fairly large dimensions of the device.
Electronic meters
The range of electronic devices is distinguished by a fairly high cost, which is fully justified by the decent quality of the device, including a higher accuracy class and the ability to function in multi-tariff mode.
The principle of operation is based on the method of converting input analog signals into a special digital code, decrypted using a microcontroller.
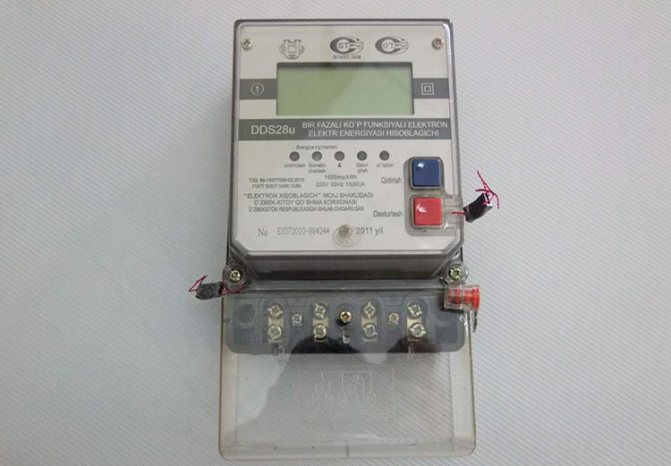

Single-phase multifunctional electronic electricity meter DDS28U
The decrypted data goes to the display or the so-called optical port. In addition to high accuracy and a multi-tariff system of use, the advantages include the ability to conduct energy metering in two directions, data storage, the ability to obtain readings remotely, as well as durability and compact dimensions.
Hybrid meters
Today, hybrid metering devices are used extremely rarely by consumers. This intermediate version of the electric energy meter has a digital interface, and the measuring part of the device can be of the induction or electronic type. Characteristic is the presence of a mechanical computing device.
Electricity meter transformation ratio 2020
Every owner, before purchasing equipment to control energy consumption, must understand that the operation of such a device will depend on the principle of operation. It is the operating principle of electricity meters that divides them into two main types: electronic and induction. Electronic electrical meters are always based on the fact that they take a direct measurement of the current and voltage on the power line passing through the system. The scale of this type of equipment is an electronic type of dial, and also has the unique ability to store the values of consumed electricity in the built-in memory.
In this type of electricity meter there are no mechanics, and the current itself will pass through microcircuits and semiconductors directly. The advantages of this type of equipment include its small size and weight, ease of connection, due to the variety of models produced. Electronic electricity meters can be manufactured specifically for one- or two-tariff accounting. They can be installed in a special automated system for commercial accounting of consumed electricity.
Despite the fact that these devices have a wider range of functionality than other types, its interface is quite simple and understandable. Thanks to the digital values on the scale, owners are able to accurately read the necessary information from the electronic meter. This type of reading equipment has a shorter warranty period because it is not as reliable as the induction type.
Induction electric meters are currently the most common. They are a mechanical structure in which two special coils are installed - for current and voltage. When this counter works, a magnetic field is formed, which sets these coils in motion. The discs, in turn, begin to move the scale with the values on the dial, which as a result displays the amount of electricity consumed.
The speed of the system will directly depend on the voltage level in the electrical network. The greater the power value, the higher the disk rotation speed. When counting, the induction type of energy supply meters has errors when counting. In order to increase the accuracy class of readings, an expensive expenditure will be required. The average service life for such equipment is usually about 15 years.
During the purchase, you can read the technical data sheet of a specific model of electric meter to find out about all the characteristics and parameters of the equipment that it has. This will allow you to choose the optimal sample for your home. The transformation coefficient of an electrical reading device does not directly relate to the design itself, but is an intermediate indicator that mainly depends on the transformer.
Experts in the field of electrical engineering note that today consumers prefer electronic types of reading devices, since their accuracy class is lower than that of induction devices. The meter's transformation ratio affects the accuracy of the final readings. On average, induction samples have an accuracy class of 2.5, while electronic samples have an accuracy class of 2.0. This means that the reading error as a result of the operation of an electronic-type electrical reading device is up to 2%, and for an induction one - 2.5%.
It is for this reason that electronic equipment is now more often installed, since it allows you to save more by getting more accurate readings. Experts strongly do not recommend installing equipment with an overestimated transformation ratio. In modern electrical engineering, it is customary to use transformers with a static CT, which is guaranteed not to change during operation.
Such electric meters include Mercury-230. Mercury-230 is produced in Russia and is considered one of the best samples for commercial and private use. Mercury-230 can be manufactured for single- and double-tariff plans. Typically, the Mercury-230 model supports a three-phase electrical network. On average, the warranty period for Mercury-230 is 25 years, which is the optimal choice when taking into account quality and price. Mercury-230 fully complies with GOST standards.
Mercury-230 has a good accuracy class and operates stably under significant changes in ambient temperature throughout the entire life of the device. Mercury-230 allows you to accurately measure the current parameters of the electrical network - frequency, power factor, current value of phase current, voltage.
Tariffizer Mercury-230 allows you to simultaneously take into account readings at 4 tariffs in 16 time zones of the day, as well as for four types of days. Mercury-230 can take into account forward active electricity and its total power by phase, the sum of the phase values with determining the direction of the total power vector.
Very often a situation arises when the owners have a transformer, but it does not have any identifying instructions or an identifier indicating the transformation ratio. During operation, the transformer reduces the current that passes through it. It is the transformation ratio of the current transformer that shows how much the value of the electric current has been reduced. It is for this indicator that a calculation needs to be made.
The transformation coefficient is designated “Kt”. When you have a device with an undefined coefficient value, then you need to pass current through it so that it is short-circuited to the secondary winding.
The calculation must be carried out with a special device, recording the amount of electric current on the secondary winding. Next, the primary current that was supplied to the primary winding must be divided by the resulting value obtained when it passed through the secondary winding. As a result, you will have the desired value of the transformation ratio of the electricity meter.
This is interesting: Calibration interval of gas meters - how to find out 2020
Typically, when using measuring equipment (multimeter or ammeter), the secondary current value is set to 5 amperes. This indicates that the current will be measured within 5 amperes. Having received this calculation, you can understand what accuracy class the reading device belongs to.
The information that you will see in the next video will not be superfluous for any man in the house. Knowing how the meter is connected and which circuit to use is a direct matter for every man.

The transformation coefficient is determined using a special formula. In apartment buildings, a large amount of electricity is consumed, therefore, to measure the amount of energy, it is necessary to resort to the use of devices that reduce (or transform) the current before feeding it to the installed common building meter. Such devices are various current transformers. In this case, the meter measures not the real energy, but the energy reduced several times. This is called the transformation ratio.
A transformer consists of two windings with different numbers of turns, which are inductively coupled to each other using an iron core. An important indicator for its operation is the transformation coefficient.
Transformation ratio is a technical quantity that shows the conversion or scaling characteristic regarding the parameters of the electrical circuit in the transformer.
In other words, this is an indicator of the ratio of the number of turns on both windings of the transformer, namely the secondary and primary. The transformation ratio determines the type of transformer, since there is a transformation ratio for both voltage and current.
Consider the types of transformers:
- A voltage transformer is used to convert voltage in circuits - high to low. It isolates the measurement and protection logic circuits from high voltage. Such a transformer is powered by a voltage source.
- The current transformer reduces the primary current to such a level that it can be used in protection and measurement circuits. This type of transformer is powered by a current source.

It is quite easy to determine the transformation coefficient after studying the theoretical part of the process
If the transformation ratio is k, and the voltage at the ends of the primary and secondary windings is U1 and U2, respectively, we obtain the following formula: k=U1/U2. In this case, the voltage on the secondary winding is determined at idle. This formula is valid for a voltage transformer.
For a current transformer, we obtain the following formula, where to determine the transformation ratio, the ratio of the values of the currents of the primary I1 and secondary I2 windings is taken, the calculation is made using the following formula k = I1/ I2.
- For a power transformer with two windings located on a single rod, the transformation coefficient will be equal to the ratio of the number of turns on the rod.
- In a transformer with three phases (three-phase), the transformation ratios can be different for phase and phase-to-phase voltages.
- The transformation ratio is equal to the ratio of the highest voltage to the lowest in a two-winding transformer.
For greater savings, the buyer is increasingly buying an electronic meter, since it belongs to the 2.0 accuracy class, and the induction one – to the 2.5 class. This indicates greater accuracy of the readings taken with its help. You can find out what it is, how it affects savings and what it shows, from electricians. In the future, you can calculate everything yourself. After all, it’s not at all difficult to calculate. There are special formulas for this.
We all know that there are two types of electricity meters: electronic and induction. The electronic meter is compact and easy to install; it also lacks mechanics. The current in it passes directly through semiconductors and microcircuits. There are also electronic meters, divided into single-phase and two-phase. With two-phase, day and night indicators are taken into account, that is, two tariffs. Note that nighttime is much less than daytime.
Therefore, many consumers use electrically consuming appliances mainly at night, for example, a washing machine, pressure cooker, etc.
The interface is quite clear thanks to the digital scale. This type of equipment has a shorter warranty period, although there are no moving parts, which increases durability and reliability.
Induction electric meters are found in every home, since they appeared long before electronic ones.:
- They have a mechanical design with two coils - for voltage and current.
- Therefore, it is quite heavy and bulky.
- The magnetic field that appears during operation of the electric meter moves these coils.
Then the disks and scale with values begin to move. After this, the amount of electricity consumed appears on the dial. The speed of operation of the entire system depends on the voltage level. The disadvantage of the device is that it is not suitable for multi-tariff metering.

When purchasing a meter, you should consult with the seller, learning about all the nuances of using the selected model
During the billing period, many users note some errors when reconciling the readings of the common house meter and their own, but this error is insignificant. The typical average service life of an induction electric meter is approximately 15 years.
To check the class of the electric meter and the actual level of power consumption, certain calculations are carried out.
- Readings are taken from the meter and multiplied by the transformation ratio specified by the common house transformer.
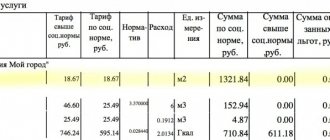
- For example, the meter reading is 70 kWh, and the transformer reduces the voltage by 20 times (the transformation coefficient is 20), then we multiply these two indicators and get the real electricity consumption (70*20=1400 kWh).
- Sometimes it becomes necessary to determine the transformation ratio in order to determine the value of the reduced electric meter by a transformer, since there is no corresponding identifier on the meter (Kt on the device).
This is interesting: Sealing an electricity meter: features, tasks, process 2020
For the calculation, a special device is used, while at the same time the magnitude of the electric current is recorded on the secondary winding. It is then necessary to divide the value (it is important that it is now obtained from passing through the second winding) of the primary current that was previously supplied to the primary winding. As a result, the required value of the transformation ratio will appear.
Typically, an ammeter is used as a measuring device. It sets a value of 5 amperes for the secondary current, that is, the current will now be measured within these limits. Using the resulting calculation, it is also determined which accuracy class the electric meter belongs to.
When selecting an electric meter, you need to pay attention to many factors, check the technical data sheet, take into account the consumer’s biorhythms, and so on. The transformation coefficient will help check the accuracy of the device, since it is used to determine the accuracy of measurements and eliminate errors.

The electricity meter transformation ratio (CT) is one of the technical quantities that affects the accuracy of the meter readings.
The indicator is determined by the operating efficiency of the transformer substation.
Let's analyze this value in detail.
Such electric meters do not have a direct connection to the home’s electrical network, which is due to the inability to connect high voltage using traditional direct-connection devices.
Thus, in order to prevent damage to meters, it is necessary to reduce the power ratings for the supplied voltage using transformer standard equipment. The choice of such equipment is directly influenced by the level of required load.
The transformation coefficient of electrical energy metering devices may vary depending on the characteristics of the installed equipment. As a result, meters for measuring electricity costs, operating with transformers, record the load, which is reduced by several tens of times.

The transformation ratio of an electricity meter indicates how many times the input parameters of voltage or current differ to a lesser or greater extent from the output parameters.
For indicators exceeding one, a decrease is made, and, conversely, for indicators less than one, a device of an increasing type is used.
Transformation ratios for voltage or current differ.
- U1 and U2 – difference in electrical voltage on the primary and secondary windings;
- N1 and N2 – number of turns of the primary and secondary windings;
- I2 and I1 – indicators of current strength in the primary and secondary windings;
- k – required CT parameters.
As a rule, such parameters of the transformation ratio are necessarily indicated in the accompanying documentation that comes with the equipment. You can also find out this information from the markings on the body of such a device.
A difficult situation is when the CT needs to be calculated independently, according to data obtained empirically. In this case, current is passed through the primary winding of the equipment and a short circuit is made on the secondary winding, after which the amount of electric current passing through the secondary winding is measured.

To clarify the real level of electrical energy consumption, it is necessary to take readings from the electric meter, and then multiply them by CT.
In practice, the CT of a transformer that reduces voltage at home is 20 units, so the data from the meter must be multiplied by this figure, as a result of which the actual electrical energy consumption will be obtained.
Meters are multifunctional devices for recording consumption, as well as storing information on electrical energy consumption. Today, three versions of metering devices are in use, designed to account for consumed electrical energy. These include induction, electronic and hybrid models. The last option is the least common.

Devices of this type consist of two coils.
The first voltage coil limits the parameters of alternating current, blocking interference and forming, in accordance with the voltage, a special magnetic flux.
The second current coil produces an alternating current.
The advantages of mechanical models include high reliability and structural simplicity, long service life, independence from voltage surges and affordable cost. When choosing induction devices, you need to take into account the fairly large dimensions of the device.
The range of electronic devices is distinguished by a fairly high cost, which is fully justified by the decent quality of the device, including a higher accuracy class and the ability to function in multi-tariff mode.
The principle of operation is based on the method of converting input analog signals into a special digital code, decrypted using a microcontroller.
Single-phase multifunctional electronic electricity meter DDS28U
The decrypted data goes to the display or the so-called optical port. In addition to high accuracy and a multi-tariff system of use, the advantages include the ability to conduct energy metering in two directions, data storage, the ability to obtain readings remotely, as well as durability and compact dimensions.
Today, hybrid metering devices are used extremely rarely by consumers. This intermediate version of the electric energy meter has a digital interface, and the measuring part of the device can be of the induction or electronic type. Characteristic is the presence of a mechanical computing device.
This is interesting: Gas meter SGMN 1 G6 - technical characteristics and advantages 2020
However, when using a large number of household appliances with different power ratings, it is recommended to give preference to three-phase meters, which allows you to connect energy-intensive devices that are designed for voltages of 220 V and 380 V.
When choosing a device, you must pay attention to the calculated current indicators, as well as the accuracy class, represented by the largest permissible relative error, expressed as a percentage.
All newly installed three-phase meters must have state verification seals that are not older than twelve months. The seal on a single-phase meter must not be older than two years.
All electricity metering devices that are designed for high currents (from 100 A and above) include step-down transformers. They reduce the current flowing directly to the measuring part. One of the main parameters for the consumer in this case is the transformation ratio of the electricity meter. It is necessary for correct readings from such measuring instruments.

Transformation ratio is the ratio of load currents and electric meter. In this case, it will always be greater than unity, since the consumption currents exceed the measuring currents. When calculating the consumed electricity, the readings on the dial or panel are multiplied by this coefficient. The resulting value is the correct number of kilowatt-hours consumed.
Transformers also have an accuracy class. For electricity metering equipment it is equal to 0.2 or 0.5. The lower the class value, the higher the accuracy of the measuring instruments.
There are a huge number of different electricity meters. However, they can all be divided into three main types:
- induction or mechanical;
- electronic;
- hybrid.
Structurally, induction meters are designed as follows - between two coils, current and voltage, there is an aluminum disk, which is mechanically connected to the scale.
The principle of operation is that current flowing through the coils creates an electromagnetic field that causes the disk to rotate. It transmits its rotation to the reference mechanism through a worm gear. The greater the current flows through the coils, the greater the inductance of the electromagnetic field, which causes the disk to rotate faster, and consequently the scale.
In the classification of meters, inductive ones are the most inaccurate. This is due to errors that arise when the electromagnetic field is converted into disk rotation. Quite serious errors can also occur in the scale rotation mechanism.
The main advantage of this type is its low price.
Electronic electricity meters appeared relatively recently. They are based on current measurement using analog sensors. Information from the sensors is sent to the microcontroller, where it is converted and displayed on the LCD display.
The advantages of electronic include:
- Small sizes.
- Ability to configure several electricity calculation algorithms.
- The highest accuracy class among other types due to the absence of a large number of elements during measurement.
- Ability to configure the ASKUE system.
The main disadvantages are the high price and greater sensitivity to sudden changes in voltage in the network.
Hybrid meters, as the name suggests, are a combination of inductive and electronic meter components. Their measuring part is taken from mechanical ones, and the processing and output of readings is carried out using a microcontroller.
This type was created in order to reduce the price of equipment that could be connected to the ASKUE system. This type is insensitive to voltage surges.
Disadvantages include large sizes and low accuracy compared to electronic ones.
As mentioned above, when calculating the consumed electricity, it is important to know the transformation ratio of the meter. Information about it can be found both in the passport for the electricity meter and on the front panel of the device. Sometimes in electronic devices it can be found in the menu. It is indicated either by a division sign or simply by a number. Typically these are values from the series 10, 20, 30 and 40.
But there are often cases when a passport for equipment is missing. In this case, the transformation coefficient can be calculated yourself. To do this, you need to have either two multimeters or special equipment.

In the first case, one multimeter measures the voltage on the primary winding, the second on the secondary. It is important to remember that measurements are made only when the transformer is idle, that is, without load. In no case should you exceed the value of the rated voltage indicated in the passport, as this will significantly increase the error.
The use of special equipment makes it possible not to use an external power source, which greatly simplifies the measurement procedure.
When measuring the transformation index, you should use measuring instruments with an accuracy class of at least 0.5.
- home
- Counter
»
Counters
How gas meters are changed: paid or free 2020
Read more
Counters
How to correctly take readings from a water meter in 2020
Read more
Counters
How does the day/night counter work? 2020
Read more
Counters
MFC - how to transfer meter readings 2020
Read more
Great article 0
Tips and tricks
However, when using a large number of household appliances with different power ratings, it is recommended to give preference to three-phase meters, which allows you to connect energy-intensive devices that are designed for voltages of 220 V and 380 V.
When choosing a device, you must pay attention to the calculated current indicators, as well as the accuracy class, represented by the largest permissible relative error, expressed as a percentage.
All newly installed three-phase meters must have state verification seals that are not older than twelve months. The seal on a single-phase meter must not be older than two years.