What does solid waste mean?
MSW or its full name - municipal solid waste - are objects of human activity that have broken down and are no longer suitable for further use. Such items are placed in the trash or redirected to a designated disposal site.
Household waste is divided into two types: organic products (this includes food) and household waste (pollutants include plastic and glass). Of the total waste, solid waste makes up twenty-five percent. Every year the amount of waste increases and causes pollution of the ecosystem.
Classification of municipal solid waste
There is a classification of waste in Russia, and certain categories of solid waste are distinguished, which are distinguished by composition and time of use.
If we consider the composition of waste, we can distinguish several categories:
- Organic waste.
- Glass.
- Metal.
- Rubber.
- Wood waste.
- Paper scraps.
- Plastic products.
- Textile.
- Leather items.
Waste use time:
- Short period of time. Non-perishable waste includes paper products and clothing.
- Long period of time. Long-term waste includes electronics products, household appliances, and auto parts.

The regulatory framework of Russia when working with waste
There are 13 current standards that clearly spell out everything about resource conservation and proper handling of waste of varying degrees of danger. Examples of some of the standards:
- GOST 30166-95 Resource saving. Basic provisions.
- GOST 30772-2001 Resource saving. Waste management. Terms and concepts.
- GOST 30775-2001 Resource saving. Waste management. Classification, identification and coding of waste. Basic provisions.
- GOST R 52105-2003 Resource saving. Waste management. Classification and methods of processing mercury-containing waste.
A list of standards has been developed and is aimed at finding application for waste in industry.
The regulatory framework of Russia related to the environmental situation is currently outdated. International law has gone much further on this issue, and amendments to laws require a modernized approach. In order for the adopted laws to make sense, we should strive to ensure that waste management acts as a separate branch of the state. Then it would be possible to more objectively consider and solve the problem of environmental pollution.
Studying the provisions in the standards, experts note that the following points are not noted in the laws that were adopted 15 years ago:
- Recycling does not have priority over disposal.
- There is no ban on the import of non-recycled packaging that acts as recyclable materials.
- The need to use available recycling technology, which is considered the best.
Threat to the environment from garbage

When household waste overloads landfills, it has a negative impact on the environment. Waste breakdown products, which can be toxic, penetrate into the atmosphere and water, and permeate the soil.
Large accumulations of household waste contribute to the destruction of the biosphere, and this threatens serious environmental problems. Land contaminated with waste prevents plant growth. Reservoirs overflowing with garbage do not fully carry out the process of evaporation from the surface of the water. And disturbances in the natural cycle lead to the following problems:
- Living organisms die.
- Diseases are spreading.
- Negative impact on climate.
- Pollution and contamination of nature.
If polymer products decompose, they are a source of toxic substances. And their impact on the ecosystem is already known. Thermal waste disposal, i.e. waste burning, is prohibited. After all, during combustion, materials decompose, and toxic elements evaporate and enter the atmosphere. Plastic products are especially dangerous when burned. Their secretions are extremely poisonous.
To avoid an environmental disaster, you should enter into agreements with organizations that carry out waste removal and disposal according to the law.
Types of waste
Until recently, all tenants paid for the removal of solid waste (solid household waste) and no one had any questions about this: everyone gets garbage, it needs to be taken out and disposed of somewhere. But with the adoption of amendments to Federal Law No. 89 “On Production and Consumption Waste,” confusion arose: the concept of MSW (interpretation: municipal solid waste) appeared, and work on their removal and disposal began to be the tasks of public utilities.
These changes came into effect in 2020. However, they should come into full force only by January 2020. Therefore, it is now not uncommon for residents of one region to pay their bills, where there is a line about MSW waste, and residents of another still receive receipts in which everything remains the same. For example, for residents of the Krasnodar Territory, Astrakhan Region, and Ivanovo Region, the payment scheme has already been changed. Therefore, at the moment there are two types of this concept:
- Solid household.
- Communal household.
The concept of solid waste
This is an integral part of the life of megacities and small settlements. This is the same garbage that accumulates in every apartment in the evening. Municipal solid waste includes:
- Biological waste: food remains, plant components, bones.
- Synthetic: plastic, cellulose, textiles, glass, metals and more.
Biological (organic) must be disposed of, because in the process of their decomposition they cause significant harm to the environment: in the process of decay, they can contaminate water and soil with the products of their decay.
And this can lead to a number of dangerous diseases. Synthetic residues take much longer to break down (some substances take more than 100 years to decompose). In addition, they often contain quite toxic substances: various dyes, oils, which eventually end up in the environment.
We recommend: Where and how to return an old car battery
Municipal household
Waste of this type is the same garbage that appears during human activity and accumulates in premises.
But this also includes goods of general consumption, which over time have lost their value in terms of utility. That is, now the official name for household waste is municipal waste, and the concept of “solid waste” now remains only in colloquial speech. It will no longer be used in official documents. Refers to MSW: garbage that is generated as a result of the activities of legal entities and private entrepreneurs, when in its component composition it is identical to ordinary household waste. At the same time, for organizations, only waste that does not appear as a result of production activities or the performance of work or services will be considered MSW:
- Residential waste, including bulky waste.
- Street trash.
- Garbage generated after cleaning parks, public recreation areas and other improvement areas.
- Plant debris generated as a result of caring for flower beds and flower beds.
- Garbage from office and industrial premises, enterprise territories.
- Garbage from airfields.
- Other types of non-toxic and low-toxic waste.
A more detailed list of what is included in MSW is presented in the Federal Waste Classification Catalog (FCCC), where each type of pollution is assigned its own code, according to which you can see whether it belongs to a particular waste group.
License
In order to engage in activities that involve the removal and disposal of waste, you will need to obtain a license. This rule is provided for in the federal law of May 4, 2011 “On licensing of certain types of activities.”
To obtain a license to work with solid household waste, you must be patient for two months. The future entrepreneur will need to acquire the necessary equipment, a conclusion from SanPin that the legal entity complies with all sanitary and environmental standards.
List of waste related to MSW with codes
Since 2020, solid household waste has been assigned the FKKO code, which should simplify the problem of its removal and destruction. Regional operators, according to the adopted amendments to Federal Law No. 89, must transport to landfills, after concluding agreements with the owners, only those household wastes that are indicated in the classifier.
Is TV included in the MSW category?
Not really
Sampling from FKKO types of waste related to MSW:
| 7 30 000 00 00 0 | MUNICIPAL WASTE, SIMILAR TO MUNICIPAL WASTE, IN PRODUCTION AND IN THE PROVISION OF SERVICES TO THE PUBLIC |
| 7 31 000 00 00 0 | Solid municipal waste |
| 7 31 100 00 00 0 | Waste from homes |
| 7 31 110 00 00 0 | Waste from homes during joint collection |
| 7 31 11 001 72 4 | unsorted waste from homes (excluding bulky waste) |
| 7 31 110 02 21 5 | bulky waste from homes |
| 7 31 120 00 00 0 | Waste from homes with separate collection |
| 7 31 200 00 00 0 | Waste from cleaning the territory of urban and rural settlements, classified as municipal solid waste |
| 7 31 200 01 72 4 | street trash and rubbish |
| 7 31 200 02 72 5 | garbage and estimates from cleaning parks, squares, public recreation areas, embankments, beaches and other amenities |
| 7 31 200 03 72 5 | waste from cleaning the territories of cemeteries and columbariums |
| 7 31 205 11 72 4 | waste from cleaning the curb area of highways |
| 7 31 210 00 00 0 | Waste from winter street cleaning |
| 7 31 211 00 00 0 | Waste from snow melting using snow melting equipment |
| 7 31 211 01 72 4 | waste from snow melting station grates |
| 7 31 211 11 39 4 | snow melting equipment cleaning sludge with a predominant content of silicon dioxide |
| 7 31 211 61 20 4 | snow melting waste using snow-melting equipment, dehydrated by natural drying, low-hazard |
| 7 31 211 62 20 5 | snow melting waste using snow melting equipment, dehydrated by natural drying, practically non-hazardous |
| 7 31 290 00 00 0 | Other waste from cleaning the territory of urban and rural settlements |
| 7 31 300 00 00 0 | Plant waste from the care of lawns, flower beds, and tree-shrub plantings, classified as municipal solid waste |
| 7 31 300 01 20 5 | plant waste when caring for lawns and flower beds |
| 7 31 300 02 20 5 | plant waste when caring for trees and shrubs |
| 7 31 900 00 00 0 | Other municipal solid waste |
| 7 33 000 00 00 0 | Industrial consumption waste, similar to municipal waste |
| 7 33 100 00 00 0 | Garbage from office and domestic premises of enterprises and organizations, classified as municipal solid waste |
| 7 33 100 01 72 4 | unsorted waste from office and domestic premises of organizations (excluding large-sized ones) |
| 7 33 100 02 72 5 | waste from office and domestic premises of organizations is practically harmless |
| 7 33 151 01 72 4 | garbage from household premises of ships and other floating craft not intended for the carriage of passengers |
| 7 33 900 00 00 0 | Other industrial consumption waste, similar to municipal waste |
| 7 34 000 00 00 0 | Waste when providing transport services to the population |
| 7 34 100 00 00 0 | Garbage and waste from cleaning railway and bus stations, airports, terminals, ports, metro stations, classified as municipal solid waste |
| 7 34 121 11 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning passenger terminals of train stations, ports, airports |
| 7 34 131 11 71 5 | estimates from the territory of railway stations and platforms are practically harmless |
| 7 34 200 00 00 0 | Garbage and waste from cleaning rolling stock of railway, road, air, and water transport, related to municipal solid waste |
| 7 34 201 00 00 0 | Garbage and waste from cleaning rolling stock of railway transport (waste from cleaning railway freight cars, see group 9 22 100) |
| 7 34 201 01 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning passenger cars of railway rolling stock |
| 7 34 202 00 00 0 | Garbage and waste from cleaning the rolling stock of urban electric transport |
| 7 34 202 01 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the electric rolling stock of the metro |
| 7 34 202 21 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the rolling stock of urban electric transport |
| 7 34 203 00 00 0 | Garbage and waste from cleaning rolling stock of automobile (bus) passenger transport |
| 7 34 203 11 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the rolling stock of automobile (bus) passenger transport |
| 7 34 204 11 72 4 | garbage, waste and in-flight catering waste from aircraft cleaning |
| 7 34 205 11 72 4 | waste (garbage) from cleaning passenger ships |
| 7 34 205 21 72 4 | special ship waste |
| 7 34 900 00 00 0 | Other waste in the provision of transport services to the population, related to municipal solid waste |
| 7 34 951 11 72 4 | unclaimed luggage |
| 7 35 000 00 00 0 | Waste from the provision of wholesale and retail trade services related to municipal solid waste |
| 7 35 100 00 00 0 | Waste (garbage) from cleaning the territory and premises of wholesale and retail trade facilities |
| 7 35 100 01 72 5 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the territory and premises of wholesale and retail trade in food products |
| 7 35 100 02 72 5 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the territory and premises of wholesale and retail trade in industrial goods |
| 7 36 400 00 00 0 | Waste (garbage) from cleaning premises, organizations providing social services related to municipal solid waste |
| 7 37 000 00 00 0 | Waste from the provision of services in the field of education, art, entertainment, recreation and sports, classified as municipal solid waste |
| 7 37 100 01 72 5 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the territory and premises of educational institutions |
| 7 37 100 02 72 5 | waste (garbage) from cleaning the territory and premises of cultural and sports institutions and entertainment events |
We recommend reading: Disposal of liquid and solid waste
Solid waste collection

The process of clearing an area of debris consists of several stages. The first is to collect waste found in residential areas. There are two options for garbage collection - separate and unitary. The names speak for themselves. If we consider separate waste collection, it depends on the type of waste. Each type of waste is placed in a separate container. With the unitary method, all types of waste go into one waste bin.
If garbage is distributed into different containers, several units of garbage trucks are provided to remove waste. This option allows you to use some waste for secondary processing.
In urban areas, garbage containers are placed in specially designated areas. There are special areas near residential areas. If these are administrative institutions, then the containers are placed at the end or between buildings, if there are several buildings.
Areas for garbage containers are placed so that it is convenient for people to approach them and for vehicles to arrive for removal.
To avoid contamination of the area with garbage, the site should be fenced with a low fence.
Sorting problems
Waste sorting exists in Russia, but is still at the initial stage of development. To solve this problem, you should take the following measures:
- Providing city residents with containers for separate waste collection, and marking what type of waste should be thrown away where.
- Using the media, inform the population about the importance and necessity of collecting waste in different containers.
- Maintain control over areas where waste is collected.
- The adoption of projects for the construction of waste treatment plants, which continued to sort waste and process it.
Types and composition of municipal solid waste
Everything that belongs to solid household waste does not pose a danger to the natural environment and people; there are no toxic chemicals or radioactive substances in this waste, and there is minimal content of dangerous heavy metals.
The classification of waste of this type is carried out on the basis of an analysis of the raw materials from which they are originally produced, the source of origin of such residues of human activity. Municipal solid waste includes end-of-use products made from the following materials:
- glass;
- paper;
- wood;
- plastic;
- metal and other types of solid raw materials.
We advise you to read: The rate of accumulation of solid waste (MSW) per person per year
MSW also includes food waste from the population, companies engaged in work in the service sector and entrepreneurs engaged in the catering sector. The growth of this sector of the economy in the regions has also led to an increase in this type of waste.
All human waste related to MSW is considered the least hazardous to the environment or the lowest hazard classes 4 and 5. While there is no sorting at the stage of accumulation in garbage containers, its processing and destruction are carried out in the most expensive ways.
Organization of waste removal
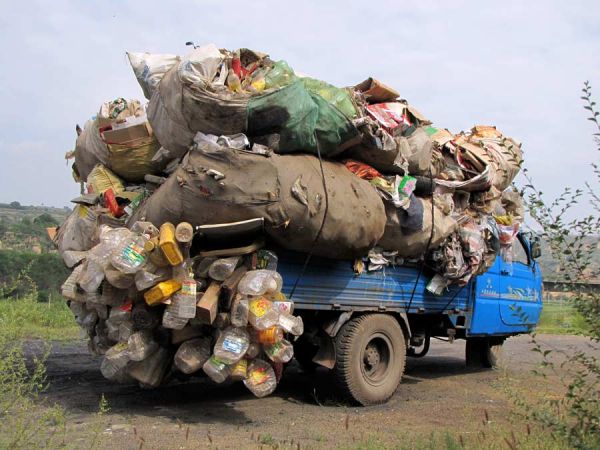

Transportation of household waste occurs through specialized transport - a garbage truck. Cars, in turn, are divided according to the following parameters:
- transport designed for the removal of waste from residential areas and large industrial waste;
- according to body capacity;
- waste loading and unloading technology;
- depending on the density of the debris.
In large cities, difficulties in removing household waste are associated with the distance that vehicles must travel to take the waste to a landfill. Many vehicles are used for commercial work, and there is simply not enough transport. When such difficult situations arise, you should make a rational decision and solve the problem. But often the solution is to raise the cost of recycling household waste.
Innovations
Previously, residents of multi-storey buildings paid for the removal of solid waste (solid waste). In 2014, Federal Law No. 458 “On Production and Consumption Waste” was amended, a new name appeared - MSW, the decoding is as follows: municipal solid waste.
But the final changes will come into force at the beginning of 2019. The law changed the persons required to remove garbage. Previously, this role was delegated to management organizations. They independently determined the cost of the services provided.
Now regional operators have been given the responsibility for removing the residues. They are developing a waste export route.
Disposal

Once the waste has been taken to a landfill, it should be disposed of. There are several common disposal methods that are successfully used in the country.
Methods
There are four main disposal methods:
- Burial. The method has certain rules that must be followed for disposal. In specially designated areas, at a great distance from residential areas, pits are prepared and filled with special solutions that are unable to release toxic substances into the soil and water. After placing the garbage there, the tank is closed. The advantage of this method is minimal costs, but the disadvantage is the penetration of toxins into the soil and vapor emissions into the atmosphere.
- Composting. This type of recycling is not yet very common in Russia. It involves the creation of compost pits, where the residues undergo biological processing and are further used as fertilizer for agricultural activities.
- Burning. This method is used in waste incineration plants. The advantage of this technology is that disposal occurs as quickly as possible, but the disadvantage is that combustion products, even taking into account the installation of purification filters, end up in the air.
- Recycling. This process involves recycling some products after the processing process.
To reuse waste, it must undergo a certain processing, which can be mechanical, biological and complex.
Mechanical processing helps to crush and compress waste, and reduce it in size by up to ten times. This makes it easier to carry out the transportation and storage procedure. But such operations help simplify recycling, but do not solve it.
Subsequent disposal
In practice, several types of processing of household waste are used: collection, sorting and direct disinfection of waste (disposal or recycling). Sorting is needed to extract from the total amount of waste those that will be suitable for use in secondary production (for example, for the same pulp and paper industry).
Disposal methods:
- Burial.
- Burning.
- Composting.
- Use as secondary raw materials.
Burial at landfills
Using landfill as a disposal method is the most cost-effective. But this method has a number of disadvantages:
- The landfill where waste is stored occupies large areas of land.
- The sites to which waste will be transported must be far beyond the boundaries of residential areas, protected areas, and recreation areas.
- The waste contained at these sites must have a low hazard class.

It should be taken into account that even low-toxic waste during the process of decomposition will have a negative impact on the soil and groundwater. And the plot of land itself on which the landfill was located cannot later be used for any economic needs.
We recommend: Household Appliance Recycling Program in Eldorado
Burning household waste
Burning is not the most harmless method, since during the combustion process many harmful gases will be released that can poison nature. Special afterburning furnaces will also be required, in which the release of toxic substances from burning garbage will be neutralized as much as possible.
The advantages of combustion include:
- The ash generated by waste disposal will take up much less space.
- Relatively low disposal costs.
- The ability to use heat energy to produce electricity or heating.
More environmentally friendly is pyrolysis, in which the combustion process is carried out without access to oxygen.
Composting method
It is only suitable for organic waste.
This method is based on the decomposition of substances under the influence of microorganisms. The advantages of this method include simplicity, financial accessibility, and the possibility of using compost as a fertilizer (used in agriculture). The disadvantage is the unpleasant odor that inevitably accompanies the process of decay. Approximately a third of all organic waste is disposed of using this method. But in order for it to be used safely, the waste must first be sorted. To achieve this, many yards began to install separate containers for plastic bottles, glass, and paper waste. In some places, separate containers are also installed for waste that may contain hazardous substances (batteries, incandescent lamps, old thermometers). All this allows you to avoid possible contamination of the environment with hazardous substances.
Recycled raw materials
The use of municipal (household) waste as recyclable materials makes it possible to produce some of the products without wasting natural resources. In addition, this reduces the amount of waste disposed of. The following can serve as recyclable materials:
- Plastic.
- Paper waste.
- Wood products.
- Glass container.
- Scrap metals.
- Various spare parts from electronic equipment.
- Petroleum products (oils, asphalt, bitumen).
Each type of recyclable material uses its own processing technology.
There are fines for non-compliance with rules regarding sanitary and hygienic conditions. All these changes adopted in legislation and relating to the normal functioning of society are designed to reduce environmental tension in the country. After all, the dirt that remains after a person and his activities is evil. And everyone will agree with this - both adults and children. Clean streets and courtyards are not only beautiful from an aesthetic point of view, they are also a sign of the well-being of society.
Equipment for working with solid waste
The following units are used to handle municipal solid waste:
- A shredder is a device that is well suited for working with fairly hard debris, such as stones. A special crushing plant helps to quickly crush waste.
- Hydraulic press - the work consists of pressing obsolete products. The units can be vertically loaded or horizontally loaded.
- Compactor - technology similar to pressing. But the unit is of impressive size and is used in large waste processing plants.
- Sorting line. Performs sorting at a waste processing plant.
- Containers located near residential buildings for collecting solid waste.
The equipment can be both stationary and mobile. Each enterprise chooses the type of units that is necessary to achieve its goals when working with waste.
How are solid waste landfills arranged?

The most common method of waste disposal in Russia is landfilling. Solid waste landfills are ravines and lowlands, special pits and quarries. The location of the polygons occurs outside populated areas.
Landfills operate a coupon system. When the customer and the contractor enter into an agreement for garbage removal, certain paper is attached. It specifies the brand of transport that will carry out waste removal, the state sign, as well as the type of waste and weight.
There are a variety of coupons depending on the type of waste. Recycling coupons are issued:
- solid waste;
- bulky waste;
- construction waste;
- soil;
- contaminated soil.
To make it easier to collect waste, they organize exchanges that include information about waste that they want to dispose of. On the same site you can find companies that deal with waste removal.
When a landfill is full and can no longer be used, the landfill is closed. After this, the land is reclaimed. This is done in order to restore the importance of the territories.
Differences between MSW and MSW
Since the innovations in the law were approved, the only correct interpretation of garbage has been in force - solid municipal waste. The abbreviation MSW ceased to be used in documentation and was preserved only in oral speech.
We conclude: there is no difference between solid waste and solid waste for citizens. However, companies transporting residues must remember that the concept of solid waste is prohibited from being used in documents.
Garbage not related to MSW is regulated by Federal Law No. 89-FZ dated June 24, 1998 (as amended on July 29, 2018) “On Production and Consumption Waste.”