The concept of a multi-circuit land plot was introduced by law recently. Previously, the term “single land use” was used in relation to such objects. The article examines the cadastral registration of a multi-circuit plot of land. This is a very important element in the implementation of land legal relations. This system guarantees owners the exercise of their rights relating to real estate, especially land plots. If this object does not have certain boundaries, then it is impossible to exercise your rights as the owner of a plot of land.
In many countries, the cadastral registration system is undergoing reform. Russia was no exception to this rule. The demand for information from the State Real Estate Cadastre is growing every year. This information acquires a new application in practice and can be used for various purposes. In our country, cadastral registration ensures the rational use of land and control that this use is carried out for its intended purpose. This principle is contained in the main legislative acts that regulate the relevant legal relations.
Concept
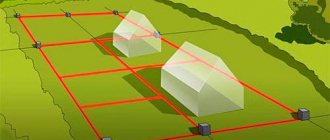
A multi-circuit land plot is a property with boundaries that together constitute several closed-type contours. Moreover, each of them does not represent a separate plot of land. The boundary of a separate contour may be the same as that of a part of a multi-circuit plot of land in the case where within the framework of this contour real rights to a multi-circuit plot of land are limited.
Each of the contours of the corresponding boundary of a plot of land is divided with other contours of the boundaries of other plots. As a result, a multi-circuit plot of land has no common boundaries. Chapter 1 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation provides for the specifics of how a multi-circuit land plot is created.
These are, in particular, the following methods for creating multi-circuit plots carried out in relation to:
- Plots in municipal or state ownership.
- From divided, allocated or redistributed plots.
Unified land use: what is it and what is it for?
Federal Law No. 221 of July 24, 2007 introduced the so-called multi-contour plots of land, which became an alternative to the use of single land use. The difference between multi-contour plots of land lies only in the presence of a slightly different classification of these land plots and the absence of cadastral numbers for isolated territories, that is, the cadastral number is assigned to the entire multi-contour plot and nothing more.
We recommend reading: How to Calculate One for Hot Water Supply
For this period of time, as mentioned earlier, unified land use is not being formed; only areas that were created earlier, before 2008, exist. Since that time, a new term has appeared - a multi-circuit plot of land. The formation of such sites is regulated in accordance with Federal Law No. 221.
Education
The formation of a multi-circuit land plot can be carried out from a combination of standard plots. According to Art. 11.6 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, amalgamation is used only in relation to adjacent areas, that is, having common boundaries. That is why the formation of multi-contour plots of land from plots that do not have common boundaries is impossible.
At the same time, if a multi-contour plot of land is registered in the cadastral register or a single land use in an earlier period is taken into account, then the creation of new plots becomes possible. In this case, a single land use that was taken into account earlier, or a multi-contour plot of land can be combined with another plot if its boundaries along at least one contour are adjacent.
What does a separate land plot included in a single land use mean?
Among the “bright” changes, it should be noted that for boundary plans for education (FormParcels) and clarification of land plots (SpecifyParcel), the ability to upload information about clarification of the boundaries and area of adjacent plots being specified (in version 4 of the scheme it was possible to clarify only the boundaries of adjacent plots): In addition , several new details have appeared in the XSD scheme and the approach to the formation of boundary plans in ARGO has changed slightly.
We recommend reading: Create a Technical Plan for a House Online
The article discusses problematic issues of the concept of “multi-circuit land plots”, which actually exist, but the term itself and its semantic content require legislative confirmation. The work provides proposals for adjusting the concept of multi-circuit land plots. Siberian State Geodetic Academy, 630108, Russia, Novosibirsk, st. Plakhotnogo, 10, candidate of technical sciences, associate professor of the department of cadastre and territorial planning, tel.
Article 11.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation
The provisions of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, which state that during division the original allotment remains within the changed boundaries, also apply to a multi-circuit land plot.
This is important to note. The created land must meet all legal requirements that are currently in force. The relevant information is specified in Article 11.9 of the Code. It is as follows:
- The maximum minimum and maximum sizes of land plots in respect of which urban planning regulations are established are determined by them.
- When creating plots, there cannot be a wedging effect, broken boundaries, the impossibility of erecting structures, interstriations and other shortcomings. This interferes with the rational use of the land, and at the same time is a violation of the requirements of current legislation.
- The limits of plots in respect of which these regulations do not apply or are not created are determined by the Land Code of the Russian Federation and other laws.
- Both the consolidation of land plots and their division, redistribution or allocation is impossible if the restrictions on them prevent their use, according to the law.
- The boundaries of allotments cannot cross settlements or municipal-type entities.
- Land plots cannot be created for individual housing construction if as a result it will be impossible to use the real estate that is located on them.
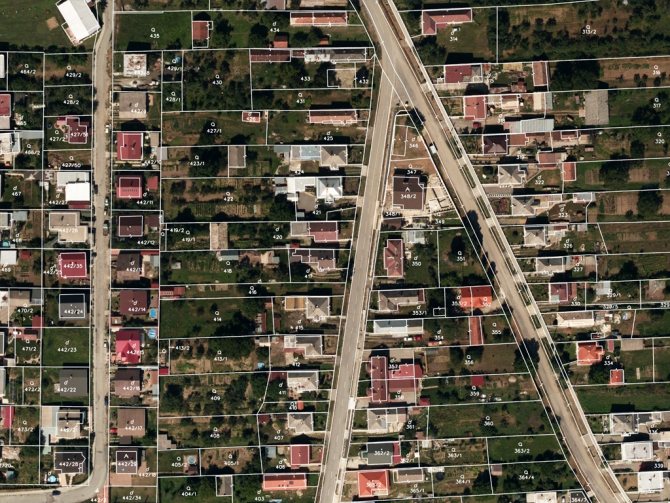

Crossing borders
This concept means the practical crossing by some contour of the border of a multi-circuit plot of land. The location of any of them outside of a municipal entity or settlement complements this definition.
All contours of the border of the corresponding plot of land may be located in different quarters of the cadastre. However, they are located on the territory of some entity or settlement (one). Thus, the location of a land plot can be characterized by the boundaries of several contours. An example of this is agricultural land used for pipelines, power lines and communication lines of other objects.
Part of a multi-circuit allotment
This object may consist of:
- One contour border. Then the part completely coincides with it or is created from its component.
- A certain number of border contours. In this case, the part coincides completely with a certain number of contours or is created from their components.
In the latter case, a part of the corresponding land is created with a border of several contours. As in the case of a multi-circuit plot, the same land surveying is applied to this part.
The new law allows this procedure to be carried out free of charge under the federal program until 2020. This is possible when purchasing or concluding a lease agreement for a municipal plot, as well as when performing complex cadastral work on large territories.
GKN
The main provisions concerning the issue under consideration are presented in the Law “On the State Real Estate Cadastre” No. 221-FZ. According to it, the State Property Committee is a systematized set of data on real estate property that is registered. This also includes data on crossing the Russian border, borders between regions, municipalities, settlements, territories with special conditions of use, and other information. The State Property Committee is a state resource of federal significance that accumulates relevant information, including the right to use a land plot in individual cases.
Cadastral registration refers to the corresponding actions of the authorized body to enter data on real estate into the State Property Committee. Through them, the presence of a particular property that has certain characteristics is confirmed, and thanks to which it can be defined as an individual thing. Relevant actions can confirm the clarification of a multi-circuit land plot, the termination of ownership of property, its existence, as well as other information.
Information on how the State Tax Committee is maintained is contained in Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation No. 42 dated October 4, 2010. G.

Legal meaning
Each cadastral number is unique, it is never repeated and belongs to a specific property; it is assigned when a land plot is registered in the cadastral register. As long as the plot exists in kind, the cadastral identification number is valid and does not change. Uniqueness is the main requirement for cadastral numbers.
The cadastral number contains encrypted data on how exactly to find a given plot. There are 4 levels in total, each of which is separated from the others by a colon: A: B: C: D, each level has a strictly defined meaning, common to all numbers:
- A – a two-digit number indicating the number of the cadastral district in the Russian Federation;
- B – a two-digit number corresponding to the number of the municipality within a given subject of the Russian Federation;
- B – number of the cadastral quarter in the form of a seven-digit number;
- G – four-digit site number.
In each of the digits, the numbering is from 1 to the maximum value within a given number. If there is no data for any digit, then the number retains the number of characters, but all of them will be equal to 0. It is best to explain using the example of a specific number: 50:05:05 17 005:0002. Here:
- 50 – identification number of the district in the Moscow region;
- 05 – cadastral number of the Istrinsky district;
- 03 16 004, where 03 is the cadastral block, 16 is the number of the cadastral array in the block, 004 is the number of the cadastral quarter in the array,
- 0002—site number.
Not only identifier functions are assigned to cadastral numbers. The code for each number is based on specific data that can be clarified, verified, and changed if necessary. If you have the cadastral number of a plot of land in your hands, then with its help you can immediately obtain the following information:
- The postal address of the site, as well as its exact number.
- Area, as well as data on adjacent plots.
- Technical information about the land.
- Assessment as of the date of entering the latest data about the site into Rosreestr.
Now no owner can make any transaction with land if data about it is not included in the cadastre. Having the exact postal address of the site, you can contact the cadastre to find out the cadastral number. However, if there are no new registration data about the plot, and the owner only has old documents with a conditional plot number, then it is from these data that you will have to start, since they have in no way lost their legal force.
The law requires that when making any transactions related to the alienation of ownership of real estate, the cadastral number of this object must be included in the documents. In other words, until the owner properly registers his land with the cadastral register, he will not be able to carry out the following transactions:
- Sell and buy land that is not registered in the cadastral register.
- Bequeath your plot to someone.
- Divide the plot into several parts, or carry out the operation of combining your land with neighboring plots into a single whole.
- Prepare a deed of gift.
- Conclude an exchange agreement.
- Rent out land.
Also on the topic: Cadastral passport for a land plot: how to get
With the entry into force of the new edition of the Land Code of the Russian Federation in Part 6 of Art. 120, a new requirement has been introduced regarding the wording of agreements for the disposal of capital buildings. Now the contract must indicate the cadastral number of the land plot on which the building is erected. In other words, even if the building has a cadastral number, but the land under it is not registered, then it will not be possible to make any transaction with this building before registering the site legally.
The owner may wish to divide the land into several independent plots. Or the owner will want to combine adjacent plots into one property. In both cases, the original object ceases to exist, and the cadastral number previously assigned to it goes into the archival database. The cadastral case itself is officially closed. Meanwhile, later, when an interested person or organization makes a formal request, information from the archived database will be provided.

Sections of the real estate cadastre
The above law on the State Property Committee contains information about what sections are available in the real estate cadastre. In particular, these are:
- Real estate register. It includes records on real estate by describing data on the corresponding objects in the State Property Committee. This information is located in the Unified State Register of Rights, where you can find out about existing and ceased to exist rights to real estate, information about this real estate and their copyright holders.
- Cadastral affairs. In this case, we are talking about a set of systematized documentation, on the basis of which the relevant data is entered into the State Property Committee.
- Cadastral maps. These are thematic maps that are compiled on one cartographic database. They reproduce information about plots of land, buildings ready and at the stage of construction in progress, borders (state, between regions, municipalities, settlements, territories with special conditions of use, cadastral division). The cadastral registration authority is authorized to maintain these maps. Information is provided to applicants without restrictions.
Record keeping
When it is necessary to enter cadastral data into the register (for example, on the right of ownership or the right to use a land plot), specialists of the cadastral registration authority carry out the following actions:
- Enter data about objects that were taken into account earlier.
- The property is registered with the State Property Committee.
- Keep records of changes to this object.
- Removed from cadastral registration.
- Indicate data according to documents that are received by the cadastral registration authority from government agencies or local authorities through an established connection of information interaction.
- Correct technical and cadastral errors.

Information status
This property information may appear in the Register as follows:
- Previously taken into account.
- Introduced.
- Temporary.
- Accounted for.
- Archival.
- Canceled.
These statuses change as a result of the adoption of an appropriate decision by the cadastral registration authority. For example, objects that have a “temporary” status change it to “registered” if the land plot is registered. In this case, the relevant information must be received from the registration authority in the order of interaction.
"Temporary" status can be changed to "cancelled" if:
- The first one has expired, but the State Committee for Taxation has not received information about registered rights to the land plot.
- The cadastral registration authority received information about the removal of the site from the corresponding registration of real estate objects, in respect of which a “temporary” status had previously been established.
- The owner or person in respect of whose plot a restriction has been established has submitted to the authorized body an application to deregister part of the land plot that has a “temporary” status.
These changes date back to the day when the employee of the authorized body made the corresponding decision or when the period of “temporary” status expired. The validity period is indicated. At the same time, this status is not assigned to structures that are under construction. Information that a land plot has been created, as well as the establishment of an encumbrance, is included in the Register with a “temporary” status.

Separate Land Plot Included in the Unified Land Use
The status of a composite plot was retained if at least 2 separate plots remained in a single land use after the division. Order No. P/119 determined that a single land use may include conditional and isolated ones. Isolated areas do not have common boundaries and can be separated by other sections or linear objects (for example, roads). In this case, conditional ones mean those that have an adjacent border, but at the same time belong to different cadastral quarters.
The program allows you to draw up boundary plans for all types of cadastral actions provided for in the form of a boundary plan: formation of land plots [1] by division, allocation, redistribution, consolidation, formation of land plots from lands, formation of parts of land plots, clarification of land plots, clarification of the boundaries of adjacent land plots, correction cadastral error.
02 Feb 2020 etolaw 1258
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Can Dad Get Maternity Leave If Mom Doesn't Work?
- When receiving the title Veteran of Labor, the title Veteran of Military Service is lost.
- Ticket price from Moscow to Tver for pensioner
- How long must a disciplinary sanction be imposed on a police officer?
Peculiarities of presenting GKN data on multi-circuit plots of land
The information contained in the State Tax Code can be provided to any person upon request. They can be prepared in one of the following forms:
- Copies of the official document on the basis of which the data was entered into the State Property Committee.
- Cadastral extract. It contains real estate data. If the object about which information is being requested no longer exists, then this document must contain information about the termination of existence.
- Cadastral passport. This is an extract from the State Property Committee, which contains the data required for state registration of a land plot in the name of a particular person, or a transaction with this plot.
- Cadastral plan. This is a thematic plan of the corresponding block or other territory specified in the request, but within the framework of the block, compiled on a cartographic base, and in which the necessary information is reproduced.
- Cadastral certificate. This is a collection of relevant data about real estate located in the territory specified in the request.
The data specified in the State Tax Code is generally provided within ten days from the date of receipt of the request. However, to provide cadastral plans or certificates, specialists are given a maximum period for preparation, which is fifteen days or thirty days from the date of receipt of the request.
If the requested data cannot be provided by law or is missing, a reasoned decision is sent to the applicant within five working days.
If a cadastral passport or extract is issued for a multi-circuit land plot, then it is necessary to indicate the number of contours of the boundaries of the corresponding plot, as well as a list of registration numbers and the area of each of them. If additional information is required, which is contained in the State Real Estate Cadastre, then it can be provided.
There are cases when the list of account numbers does not fit in the appropriate section. Then you can draw it up on another sheet, where the list is made in the form of a table indicating the area of the land plot and possible notes. This sheet must be signed by an authorized person and have the seal of the authority issuing the document.
When a cadastral passport or a corresponding extract of a multi-contour plot of land is drawn up, a plan of this plot is displayed on such a scale that the readability of the inscriptions on the image is ensured. If it was not possible to place an entire section on one sheet, then this is done on several sheets, including using insets.
The amount of necessary data provided by the State Committee for Taxation can be indicated by the applicant in the corresponding request. If data is required for recorded land uses, the document provided will refer to the area as a “single land use”.
Plots for which cadastral registration was carried out before the law on the State Property Committee came into force (for example, land plots for individual housing construction) are called “previously registered”. Data about them must contain information that is available in documents issued by the State Real Estate Cadastre. But regardless of whether data is required on a multi-circuit plot of land or previously registered plots, the information is provided in the form of a cadastral passport or an extract in relation to real estate, the right to which arises after state registration. However, the same information in relation to a site that is part of a single land use is not provided.
What is this?
The Russian unified real estate accounting system uses digital expressions, where each group of numbers has a strictly defined meaning. For example: AA:BB:CCDDEE:FF, where
- AA – district;
- BB – district;
- CCDDEE – quarter;
- FF – number of the land plot within the block.
Confirmation of ownership is an extract from the Unified State Register, which must indicate the cadastral number, by which any interested person or agency finds out the exact data about the plot, its owner, and the value as of the date of registration.
Until a property is entered into the Rosreestr database, it does not have its own code. Until this moment (before registration), the object is designated by a conditional number. This procedure was introduced by Federal Law No. 122, which governs the activities of the state cadastre.
It also happens that in the registration documents for a plot there are two numbers at once - the previous conditional one and the new cadastral one. This is the correct approach, since until the completion of registration activities, the property appears in the information databases under a conditional number. In other words, the conditional number has serious meaning.
Both conditional and registration cadastral numbers have a similar structure, where specific information is hidden behind groups of numbers. It is also worth considering that once assigned a cadastral number never changes to another, except in cases where a property is liquidated, being divided into several independent objects or annexed to a neighboring one.
Currently, all real estate objects that are newly created and entered into the register under cadastral numbers do not have conditional numbers, however, the base of these numbers remains very large.

How to identify a conditional cadastral number?
The most important difference between the conditional number is its greater length. Until a unified cadastre database was created, conventional numbers had additional identification marks that marked extensions and other objects related to the main property. Currently, any building is entered into the cadastre under its own number. The conditional number contains the following designations:
- Region.
- District.
- Quarter.
- Real estate object.
- The serial number of the building.
The cadastral number consists of 4 groups of numbers separated by a colon. The conditional number may have a larger number of digits, since additional objects are attached to the main structure. Of course, this rule does not apply to plots, since any of them is a single indivisible whole.
Which number is more reliable: cadastral or conditional?
The registration cadastral number is more reliable, since before the data on the site enters the cadastre, the boundaries are clarified and land surveying is carried out, and these land management works are carried out in the current coordinate system.
Also on the topic: Recognition of ownership of a land plot: by inheritance, by privatization, through the court
Previously, when sites received conditional numbers, it was not necessary to carry out such a volume of work without fail, which is why there are so many factual errors in the old data. Now it is impossible to conduct a real estate transaction in full compliance with current legislation without the registration cadastral number of the plot.
But that's not all. After all, old conditional numbers often exist only on paper in a single copy. The loss of such papers makes it impossible to recover lost information.
Conditional numbers of plots in SNT
Since 2020, in accordance with Federal Law No. 221, cadastral registration has been introduced throughout the Russian Federation. Any real estate, including plots in SNT, are subject to registration. Conditional numbers are valid until the object is properly registered. Considering how many areas are still being prepared for registration, there is no reason to expect that the procedure will be completed 100% in the very near future. Although, the owners themselves are certainly interested in completing registration as quickly as possible.