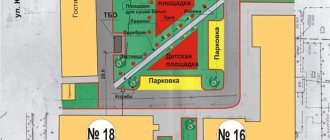
Who is responsible for the local area of an apartment building?
The law has a single opinion on this matter - it is either the Management Company or another organization hired by the Homeowners Association - if it is the legal owner of the area adjacent to the house, and for this a number of requirements must be met.
But first things first. First you need to define the concept. This is what is included in the designated territory (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 491 of 08/13/06):
- a plot of land where the house stands, and its boundaries are determined by the Cadastral Chamber;
- green spaces;
- garages;
- children's towns;
- fire passages;
- clothes dryers;
- thermal installations;
- parking;
- sports grounds.
In a word - those objects within the boundaries of the site, the purpose of which is to serve the needs of this apartment building and those who live in it (Article 36 of the Housing Code.)
The area of this plot, as well as everything that is included in it, is indicated in the Cadastral passport.
If this piece of land is not properly registered and does not have a cadastral passport, then the responsibility for caring for it falls on the shoulders of the municipality. The initiators of registering a plot of land for cadastral registration must be the owners themselves - the head of the HOA must apply to the municipality.
Definition of the local area
The adjacent territory is a piece of land on which an apartment building and the territory adjacent to the building are located. The main characteristics of this object are contained in the cadastral register. You can find out about them by receiving an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. Also, the main characteristics of the territory adjacent to the house are prescribed in the technical documentation of the land plot and building.
Based on these parameters, the organization managing the common property calculates the costs of sanitary maintenance and improvement of the local area.
If documents for the local area have not been drawn up or errors were made during their execution, the responsibility for maintaining such a land plot rests with the administration of the locality.
The main legislative act regulating the use and ownership of real estate, in particular an apartment building and the plot of land on which it is located, is the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. The rules of law regulating these issues are also contained in other acts in force on the territory of the Russian Federation. Article 16 of Law No. 189-FZ of December 29, 2004 determines that the land plot on which the apartment building and other related objects are located is in the common shared ownership of the owners of the premises in the building.
The shares of each such owner are determined in proportion to the area of the premises owned by him. Each part of the land plot is an integral part of the local area and cannot be sold or transferred to any of the residents for sole ownership.
The local area may include the following objects:
- the land plot itself on which the building is located. Its configuration and main parameters can be found on the public cadastral map by the cadastral number of the object;
- structures and elements that improve and green the local area;
- objects that are necessary for the maintenance of the house and the comfort of its residents.
The area of the land plot allocated for the local area may vary. But as a general rule, it should not be less than the area of the building located on it.
Who pays the costs?
The financial maintenance of the territory is the responsibility of those who own the house - that is, the owners of the apartments. From the moment the plot is registered with the cadastral register and a cadastral passport is received for it, the adjacent territory becomes the shared ownership of the residents. Maintenance is provided at their expense.
After the area adjacent to the house is registered in private hands, the HOA will be able to dispose of it as it chooses. For example, arrange children's playgrounds, plant flower beds, build a parking lot intended only for the inhabitants of this house.
You can even fence the area to limit access to it by unauthorized persons, but this should not impair the freedom of movement of other citizens. And secondly, it must be agreed with the municipality. If fences are erected without permission, such fencing is subject to demolition.
In addition, barriers:
- must have controlled passage and open at any time of the day;
- should not interfere with the passage of public service vehicles, such as emergency or ambulance services, as well as access of the management company.
The same applies to parking. In addition to the need to comply with SanPin requirements, you should also remember that even a closed parking lot should have free access for emergency services, such as the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
However, regardless of what will be built in this area and whether it will be built at all, the obligation of apartment owners remains the same - to keep the area clean and tidy.
If the territory is not registered as private property, its improvement is carried out at the expense of the municipal budget.
List of works and payment
The surrounding area must be properly maintained. The list of works and activities that must be carried out within the framework of this content is regulated by the following legislative acts:
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 3, 2013 No. 290.
- Resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 No. 170.
The list of required works includes:
- cleaning common areas;
- arrangement of waste containers and their locations, as well as timely waste removal;
- planting and caring for them;
- arrangement and repair of recreation areas for residents;
- cleaning and repairing fences, benches and other objects;
- ensuring the cleanliness of the parking lot;
- disinfection;
- snow and water removal;
- ensuring the safety of residents under certain weather conditions. This may include clearing ice from paths and steps, sprinkling sand or other mixtures of passage areas;
- mowing grass on lawns.
This list is not exhaustive. At the general meeting of owners, residents can supplement it by making a decision by voting.
Also, the owners of premises in an apartment building at a meeting have the right to determine which activities to entrust to the management company, and which ones to carry out and pay for as necessary, hiring third-party organizations. In order for such a decision to be made, it is necessary to obtain at least 2/3 of the votes of the participants.
The legislation delineates responsibilities for cleaning the territory in the following order:
- the territory between apartment buildings, in particular, playgrounds and driveways, must be cleaned by the management company;
- roads within neighborhoods are cleaned by city organizations;
- First, paths and sidewalks are cleared, then roads.
Activities related to the maintenance of the local area are paid for by residents. This obligation is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, in particular, the Housing Code. According to this regulatory act, property owners are required to maintain it, as well as common property, in full.
From the moment the land plot adjacent to the house is registered in the cadastral register, the territory becomes the shared property of the owners of the premises in the building. Financing of events is carried out by the owners, depending on the size of their shares.
If the land plot of the apartment building is not formed and the administration of the locality does not take any action to correct this situation, responsibility for the maintenance and improvement of the local area rests with it.
Since in most cases the management of the house is carried out by the management company, the costs of maintaining the local area are included in the receipt for utility bills.
What is included in the content?
So, the responsibilities of the management company for maintaining the local area of an apartment building include:
- maintaining the cleanliness of the parking lot;
- planting flowers and caring for them;
- garbage removal;
- cleaning public areas;
- disinfection;
- allocation of a special place and equipment of garbage boxes;
- removal of snow, rain and melt water;
- lawn care;
- arrangement of areas for children's recreation - slides, sandboxes, etc.;
- repair and cladding of gates, facades;
- regular garbage collection, snow removal, sprinkling icy paths with sand in winter.
At the meeting of apartment owners, the residents themselves make decisions regarding financing, as well as the distribution of responsibilities - what to delegate to the Management Company, why it is better to hire a third-party organization, etc. The decision must be approved by two-thirds of the votes of those participating in the meeting.
Cleaning of sites, passages between houses and generally whatever the HOA decides is carried out by the Management Organization. The same applies to cutting down trees and mowing grass. Specialized organizations manage roads within neighborhoods
Sanitary maintenance of the local area (types, composition and frequency of work)
1. Sanitary maintenance of the local area
(types, composition and frequency of work)
| No. pp. | Types of jobs | Scope of work | Frequency of execution |
| 1 | Sweeping the land in summer | Sweeping the area, cleaning and transporting waste to the designated location - asphalt pavement | Necessary |
| 2 | Same thing - ground cover | Necessary | |
| 3 | Removing debris from lawns | Removing debris, branches and leaves from lawns | 3 times a week |
| 4 | Cutting grass | Seasonal lawn mowing | 1 time per season |
| 5 | Shifting and sweeping snow in the absence of snowfall | sweeping freshly fallen snow, moving freshly fallen snow with an engine into shafts and piles - asphalt pavement | 1 time every 2 days |
| 6 | The same - ground cover | 1 time every 2 days | |
| 7 | Shifting and sweeping snow during snowfall | Sweeping freshly fallen snow, moving freshly fallen snow with an engine into shafts and piles - asphalt pavement | Once every 3 hours |
| 8 | The same - ground cover | Once every 3 hours | |
| 9 | Sprinkling the area with sand | Sprinkling the area with sand | 1 time every 2 days |
| 10 | Clearing ice from porches and walkways | Clearing ice from porches and walkways | 3 times a month |
| 11 | Mechanized cleaning of the local area (sidewalks) from snow in winter and leveling in summer when adding ASG | Mechanized cleaning of the local area (sidewalks) from snow in winter and leveling in summer when adding ASG | 2 times per week |
| Additional work (at the request of the customer) | |||
| 1. | Cleaning cells | Once a week - dry cleaning, 2 times a month - wet cleaning | |
| 2. | Replacing electric light bulbs in the entrances (issued the entrance to the senior person against signature) | 1 time per month |
2. Preparing an apartment building
for seasonal use
Work to prepare apartment buildings for the spring-summer period includes:
— strengthening drainpipes, elbows, funnels;
— filling potholes in the stone steps of the porches;
- removing springs on entrance doors
The table shows the scope of work to prepare houses for the spring-summer period.
Preparing a residential building for the spring-summer period
(composition, types and frequency of work)
| No. pp. | Types of jobs | Scope of work | Frequency of execution |
| 1 | Strengthening drainpipes, elbows and funnels | Replacement of some of the stirrup grips and plugs, removal and installation of new grips in the old sockets with preparation and replacement of plugs if necessary, strengthening of drainpipes, elbows and funnels to the grip with wire or clamps | 1 time per season |
| 2 | Filling potholes in stone porch steps | Inspecting porches, clearing cracks or broken places on steps, cleaning repair areas, sealing repaired areas with mortar and grout | 1 time per season |
| 3 | Removing springs on entrance doors | Removing springs on entrance doors | 1 time per season |
Work to prepare apartment buildings for the autumn-winter period includes:
— repair and strengthening of entrance doors;
— checking the condition and repair of vents in the basements of buildings;
— replacement of broken glass windows and doors in common areas.
Preparing a residential building for the autumn-winter period
(composition, types and frequency of work)
| No. pp. | Types of jobs | Scope of work | Frequency of execution |
| 1 | Repair and strengthening of entrance doors | Small and large repairs of door panels: removing the door panel, cutting and fitting the door panels to the opening; installing the bar; sealing sockets after removing locks; preparing strapping bars according to size and profile manually; repair of door purlins; strengthening door frames; hanging the door leaf on the hinges. changing door hinges: removing the door leaf; removing hinges and unscrewing screws; sealing holes for screws or sockets for hinges. Change of door devices (handles, springs, locks). Box repair: straightening box distortions with wedges; securing the box with additional ruffs, attaching quarters of the box. Changing the door block. | 1 time per season |
| 2 | Checking the condition and repairing vents in building basements | Inspecting the vents, clearing cracks or broken places on the vents, washing the cleared areas, sealing the repaired areas with a solution and grout. | 1 time per season |
| 3 | Replacing broken glass and doors in common areas | Removing glass with cleaning the folds and removing beads, Cutting and trimming glass, coating glass folds or lining with wire, inserting glass with strengthening them and installing beads, wiping glass | 1 time per season |
3. Maintenance of in-house engineering equipment of residential buildings
Maintenance of in-house engineering equipment of multi-apartment residential buildings includes the following types of work:
— repair, adjustment, testing, reactivation of central heating systems;
— grinding in shut-off valves without removing them;
— compaction of squeegees;
— packing seals of shut-off valves to eliminate leaks on pipelines with a diameter of up to 30 mm:
— stuffing of oil seals in water supply systems;
— temporary sealing of fistulas and cracks on internal water pipes and risers with a diameter of up to 50 mm;
— eliminating leaks in pipelines with replacement of pipe sections;
— cleaning steel pipes with a brush;
— inspection of cold water supply valves;
— insulation and cleaning of smoke ventilation ducts;
— carrying out technical inspections and eliminating minor faults in the ventilation system;
— packing seals for cold water supply;
— cleaning and flushing of sewerage outlets;
— carrying out technical inspections and eliminating minor faults of electrical devices;
— replacing burnt out light bulbs in the basement and attic;
— replacement and repair of switches;
— replacement of circuit breakers.
The composition and frequency of maintenance work on the in-house engineering equipment of multi-apartment residential buildings are shown in the table.
Monitoring of technical condition is carried out through scheduled inspections using modern technical diagnostic tools.
Routine inspections are divided into general and partial.
During general inspections, the technical condition of the building or object as a whole, its systems and external improvements is monitored; during partial inspections, the technical condition of individual premises structures and elements of external improvements is monitored.
General inspections, during which the scope of work is specified for inclusion in the routine repair plan, are carried out once a year.
When carrying out partial inspections, faults are eliminated that can be eliminated during the time allotted for the inspection.
Maintenance of in-house engineering equipment of residential buildings
(composition, types and frequency of work)
| No. pp. | Types of jobs | Scope of work | Frequency of execution |
| 1 | Repair, adjustment, testing, reactivation of central heating systems | Strengthening hooks for pipes and central heating devices. Elimination of air pockets in the heating system. Preservation and re-preservation of the central heating system: inspection of the central heating system, including checking the condition of the pipeline, heating devices, control and shut-off valves, and fasteners. Checking the condition of hangers and gaskets - supports for the main pipeline, expansion tanks in the attic. Drawing up an inventory of deficiencies, carrying out the necessary repairs. Flushing the system under pressure. Connecting the hose to the pipeline. Disconnecting the hose from the pipeline. Test fire. Checking thermal insulation and minor insulation repairs. Replacement of individual sections of pipelines. Installation of valves for bleeding air from the system. Insulation of central heating pipelines and water tanks. Restoration of destroyed thermal insulation, Pipeline testing. Draining the system water. Pressure testing of the system. Filling the system in the forehead to a given pressure. | 1 time per year |
| 2 | Grinding in shut-off valves without removing them from their place | Shutting off the water, removing the oil seal and old packing, packing the oil seal and installing the oil seal in place with tightening the nuts, grinding in the stopcock and valve at the valve, starting the water | 1.33 times per month |
| 3 | Compaction of squeegees | Compacting squeegees using strands or asbestos cord | 1.33 times per month |
| 4 | Packing of seals of shut-off valves with elimination of leaks on pipelines with a diameter of up to 30 mm | Packing seals of shut-off valves to eliminate leaks in pipelines | 1.33 times per month |
| 5 | Packing of oil seals in water supply systems | Closing the apartment valve, removing the handwheel and stuffing box head, packing the stuffing box, installing the nut and handwheel in place, opening the apartment valve, checking the operation of the tap | 1.33 times per month |
| 6 | Temporary sealing of fistulas and cracks in internal water pipes and risers with a diameter of up to 50 mm | Cleaning the sealing areas, installing an elastic lining, securing the clamps to the bolts | 1.33 times per month |
| 7 | Elimination of leaks in pipelines with replacement of pipe sections | Cutting out an unusable section of pipe, installing a new section using welding, cleaning the welding area | 1.33 times per month |
| 8 | Brush cleaning of steel pipes and fittings with a diameter of up to 50 mm | Cleaning steel pipes and fittings with steel brushes | 1.33 times per month |
| 9 | Inspection of valves for cold water supply | Disassembly of valves, assembly, lubrication, cleaning, stuffing, checking | 1.33 times per month |
| 10 | Insulation and cleaning of smoke ventilation ducts | Cleaning clogged smoke ventilation systems, removing blockages with checking the channels, punching cleaning holes in the channels as necessary, sealing cleaning holes, plastering the sealing areas. | 4 times a year |
| 11 | Carrying out technical inspections and eliminating minor faults in the ventilation system | Checking the serviceability of hoods, cleaning the ventilation ducts: removing the ventilation grille, removing blockages within reach and checking the ducts, installing the ventilation grille in its original place. | 1 time per month |
| 12 | Packing oil seals for cold and hot water supply | Removing the oil seal and old packing, packing the oil seal and installing the oil seal in place with tightening the nuts | 1.33 times per month |
| 13 | Cleaning and flushing of risers and sewer outlets | Cleaning and flushing of risers and sewer outlets | 1.33 times per month |
| 14 | Carrying out technical inspections and eliminating minor faults of electrical devices | Checking the grounding of the electrical cable sheath, measuring the insulation resistance of wires in common areas and basements; strengthening electrical wiring; Troubleshooting minor electrical problems | 4 times a month |
| 15 | Replacing burnt out light bulbs in the basement and attic | Removing the lampshade if necessary, unscrewing the burnt-out light bulb from the socket, screwing in a new light bulb, checking operation | 1 time every 3 months |
| 16 | Replacement and repair of switches | Replacement and repair of switches | Necessary |
| 17 | Replacing circuit breakers | Replacing circuit breakers | Necessary |
4.
Other types of work for the maintenance and repair of the common property of an apartment building
When operating residential buildings, the following types of work (costs) are also taken into account:
— carrying out deratization
by treating premises in residential buildings (attics, basements) using poisoned baits;
— carrying out disinfestation
by treating premises with the use of special means (insecticides) to kill insects;
— emergency maintenance of residential buildings
, which includes the performance of work related to the elimination of accidents and malfunctions of in-house equipment on sewerage networks, cold and hot water supply, central heating, electricity and gas supply - is accepted in an amount that ensures the maintenance of the necessary personnel (dispatcher, plumbing service specialists, gas service foreman, UAZ) under a contract with a specialized organization;
— maintenance of indoor gas equipment
and networks - under a contract with a specialized organization;
— payment for electricity for common areas (l/cells)
— according to the accounts of the energy supply organization;
— expenses for cash settlement center services
on charging for housing and communal services; collection of funds from the population for housing and communal services, accrual of benefits to categories of persons entitled to this according to the current legislation - accepted in the amount of 1% of the estimated value of tariffs for housing and communal services provided by the management organization to consumers;
— intermediary services
for the supply of utilities.
5.
Management
Includes the content of the director, engineer, chief. accountant, legal advisers, supervisory technicians, payroll accountant, personnel, supply and accounting specialists - 12 people in total. Work composition:
Get full text
Management of all types of enterprise activities in accordance with current legislation.
Organization and maintenance of accounting in accordance with the unified methodological principles of accounting and reporting on the territory of the Russian Federation for organizations that are legal entities.
Planning of financial and economic activities. Organization of labor and wages of enterprise employees.
Providing personnel with the required qualifications and specialties, organizing educational and methodological work on the necessary types and forms of training and advanced training of enterprise employees.
Documentation of management decisions, actions, connections; organization of document flow; organizing and storing documentation; control of timely execution of orders, instructions and instructions; technical maintenance of the work of the head of the enterprise.
Providing the enterprise with all the material resources necessary for its activities, receiving, storing and dispensing inventory and material assets; control over their use. Housekeeping of buildings and premises in accordance with the rules of industrial sanitation and fire safety.
Monitoring the state of labor protection at the enterprise. Organization of briefings, training, testing of knowledge on labor protection of enterprise employees.
Conclusion, renegotiation, termination, legal registration of contracts, monitoring the fulfillment of contractual obligations. Preparation of materials for transfer to arbitration, investigative and judicial authorities, recording and storage of copies in progress and completed in the execution of judicial and arbitration cases.
Carrying out servicing of personal electronic computers and organizational equipment. Maintenance of software.
Work with the public, including consideration of requests and complaints regarding the quality of service.
Registration of the local area as collective property
Land surveying is the first step for residents to privatize their local area. And, strictly speaking, the only one.
Back in 2010, the Constitutional Court recognized a special procedure for transferring ownership of land under any multi-apartment building to apartment owners.
Unlike the privatization of lands for other purposes, after a new land plot is allocated and registered in the cadastral register by an act of municipal authorities or at the request of home owners, the right to it automatically passes to the owners of the house.
Obtaining land ownership has a number of undeniable advantages:
- by decision of the general meeting, it can be used for profit - rented out;
- the city cannot build anything on such a site without the consent of the legal owners;
- If it is necessary to use the local area for public needs, the municipality can only purchase the site or part of it.
This is important to know: registration of the adjacent territory of an apartment building as property
In addition, you will need to pay land tax annually. The amount will have to be calculated independently and then distributed proportionally among all owners. The larger the area of the occupied apartment or commercial premises, the higher the tax will be.
Legal problems
- determining the size and boundaries of the PT;
- nature of use;
- management features.
The fact is that common property belongs to everyone. This means that while a person has the right to use and dispose of property, he cannot do anything alone. All decisions regarding PT are made only by a majority vote at the general meeting.
This is how the peculiarities of managing local areas manifest themselves. At the general meeting, residents decide on the placement of new facilities not included in the project, the allocation of plots for parking, landscaping, and recreational areas.
The main legal problem is determining the boundaries and area of the local area. The fact is that such territories were not allocated for houses of old construction. Yes, some buildings and courtyards did not have, there were only streets and areas like a well. Since buildings built before the nineties of the twentieth century were in state ownership, issues of development of adjacent areas were resolved at the level of local authorities.
For this reason, there are many buildings in cities that formally do not have adjacent areas. Sometimes there is simply nowhere to form them. At the same time, there is a method for calculating PT in accordance with the total area of the apartments of a given building. In order for a house to have its own official local area, property owners need to hold a general meeting (the quorum is two-thirds of the total number of owners), make a decision and contact the municipal authorities with a request to carry out land management work.
Land managers must not only determine the area of the PT, but also mark it on the ground. This will be useful for further actions on the use of land owned by the owners of the apartments of this building. After carrying out the work and receiving the technical plan, a package of documents is submitted to the Rosreestr authorities. If the applicants are denied registration of the PT as part of the property, then such a decision can be appealed in court.
Rules for placing objects
Everything that is located in the local area is a consequence of the implementation of the project, the decision of the residents of the house, or the illegal actions of people who want to benefit. After the house is built and put into operation, the so-called landscaping is carried out. The objects provided for by the project must be handed over along with the house. Everything else is finalized by the owners.
The biggest problem in the courtyards of urban apartment buildings is parking. Older houses were not designed for a large number of cars. Moreover, historical buildings were generally erected without taking into account the availability of personal transport. For this reason, when managing local areas, the organization of parking spaces is of great importance.
Who serves the territory
The fact that the adjacent territory belongs to all apartment owners does not mean that they all service it at once or in turn, although this is also possible. By decision of the general meeting, apartment owners choose a management company that not only ensures the viability of the house, but also maintains the surrounding area in proper order.
The scope of work depends on the agreement between the residents and the management company. However, usually such an organization carries out work on:
- cleaning the area;
- arrangement of recreational areas, including children's playgrounds;
- the formation of areas with green spaces;
- repairing roads in the yard;
- care of all PT facilities.
So, when choosing a management company and concluding an agreement with it, residents need to carefully consider all the points of mutual obligations.
If the local area is not allocated or some of the objects are, by force of circumstances, owned by the municipality or some department, then the general meeting or initiative group will have to interact with the management of the institutions, forcing them to take the necessary actions. If there is no provision in the agreement for maintenance, for example, of the road and sidewalks, the issue of a one-time event to pay for road repair work at the expense of the residents of the house will have to be put on the agenda of the general meeting.
This is important to know: How to privatize a garage and the land under the garage into ownership
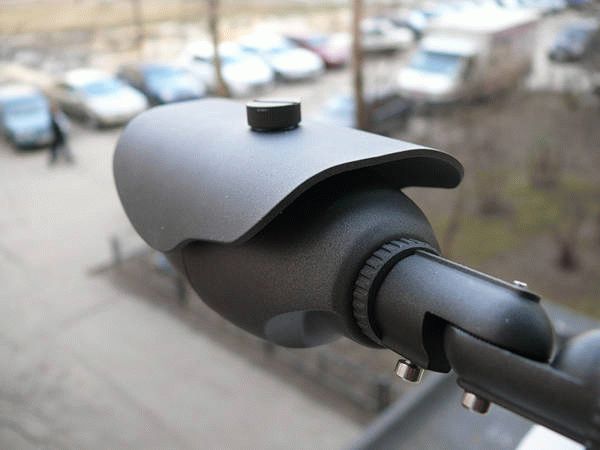

You will have to equip the yard with video cameras yourself. To do this, you can enter into an agreement with an organization working on the “safe yard” project. The agreement can be concluded either with an individual or with the owners of several apartments. The advantages of this project are that with the help of a video camera placement system it is possible to cover almost the entire local area with round-the-clock surveillance.
Territory demarcation
Despite the fact that each apartment building has a specific territory, it is not always clearly marked out and formalized. According to the law, registration of the local area is carried out in 3 ways - one applies to new houses, the other two - to secondary housing (if the territory is marked in the cadastre and if the registration of the site has not yet been carried out).
To clearly identify the area around the house, it is necessary to carry out land surveying. The need for it usually appears in cases where the management company or residents begin to think about the rational use of the site. All objects around the house (gazebos, benches, platforms, etc.) are initially intended for use only by apartment owners. However, in reality this is often not the case. Despite the contribution of funds for maintenance and improvement by very specific residents, these benefits are available to everyone without any restrictions.
To avoid such situations, the management company, at the initiative of the owners, begins to allocate this territory. This procedure is carried out by specialized organizations working with the cadastre. They are involved if there is an appropriate decision made at a general house meeting. Trained specialists begin surveying the property. Avoidable mistakes are often made during meetings.
Please note that land surveying for existing houses in big cities is rarely required. For example, in Moscow, with its high cost of land, every square meter of urban territory is distributed and has its own owner. Most often, this procedure is requested when documents are lost. In other situations, information about the size of the local area can be clarified in Rosreestr.
Land surveying specialists are involved in cases where there is no information about the land owned by the house. The engineer measures the territory adjacent to the apartment building and hands over a disk indicating its boundaries. This media, along with a package of documentation, is sent to Rosreestr or MFC for registration of a cadastral plan.
In order for the responsible authority to prepare such a plan, it must be provided with:
- statement;
- minutes of the general meeting;
- disk from a cadastral engineer.
The period for preparing a cadastral plan is limited to thirty days. As soon as this document is in hand, you can use the territory indicated in it.
This is interesting: Land tax in program 1C 8.3
Management organizations should remember that it is impossible to abandon the territory after land surveying. Sometimes this turns out to be an unpleasant surprise. For example, a cadastral engineer may classify a part of an abandoned vacant lot as a house, which no one has paid attention to for many years. After land surveying, the site will have an owner, and local authorities will have the right to require him to maintain the land in accordance with the requirements for improvement.
Based on the results of land surveying, the management organization, by decision of the owners, can:
- mark the boundaries of the adjacent territory of an apartment building with a fence; according to the laws and regulations in force in 2020, its height should be no more than 20 cm;
- place a barrier at the entrance in agreement with the traffic police, fire departments and other authorities;
- start creating recreational facilities, sports grounds and other infrastructure elements;
- erect the necessary outbuildings;
- transfer part of the territory to tenants;
- arrange a parking lot for the owners' cars, pave it and mark it;
- plant flowers or other plants.
In some cases, apartment owners may refuse the adjacent territory. This is usually due to reluctance to pay for its maintenance. If residents refuse to own and dispose of the land around the house, then a perimeter is maintained behind the building, spaced 5 meters from its walls. This is a regulatory requirement laid down in legislation. The rest of the land goes to the city, which can dispose of it at its own discretion. For example, authorities can transfer land to tenants who will build shops or arrange paid parking lots.