Debts for housing and communal services, responsibility
The current legislation clearly states the obligation of residents to promptly pay for used utility resources, as well as pay rent. This conclusion is confirmed by clause 1 of Art. 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, which states that citizens and organizations must make payments for housing and communal services strictly on time.
In addition, the law specifies a specific period before which payment must be made. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 155, money is paid monthly before the 10th day of the month following the period for which you need to pay.
In case of delay, the following measures may be applied to debtors:
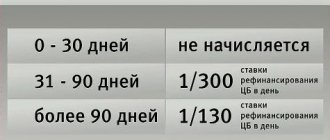
- Accrual of penalties (Clause 14, Article 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) - its size depends on the duration of the period during which the owner of the premises did not pay off the housing and communal services debt. There are two possible options:
- 31-90 days – the amount of the penalty is 1/300 of the key rate (refinancing) of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which is in effect at the time of payment. It is calculated based on the total amount of debt for each day of delay.
- 91 or more - in this case the penalty will increase and amount to 1/130 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The calculation is carried out in a manner similar to that indicated above.
- Limitation of the supply of a utility resource for which there is a debt (clause 114 of Section XI of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 6, 2011 No. 354) - in this case, the resource supplying organization temporarily reduces the volume of supplied utility services, while establishing an appropriate schedule. Before applying this measure, the executor must notify the debtor about this.
- Termination of the provision of utility services (clause c) clause 119 of section XI of the above-mentioned Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation - when using such an enforcement measure, the supply of housing and communal services to the apartment for which there is a debt is completely stopped. The supply of an apartment with one or another type of utility resource can be stopped if the debtor has not repaid his debt within 10 days after the restriction was introduced.
How to pay penalties through Sberbank Online
One of the most popular and convenient functions available to users of the Sberbank Online service is the ability to pay penalties and fines to various government bodies. It is worth considering what actions need to be taken and what to pay attention to when paying fines through Sberbank Online.
Payment of fines and penalties through Sberbank Online: step-by-step instructions
In order to pay a fine or penalty, you need to carry out the following sequential actions:
- Log in to your Sberbank Online personal account (if it has not been created, then you need to open it).
- Select the card from which payment will be made.
- In the bank card field, select the type of operation using the “Operations” button.
- By clicking on the “Operations” button in the menu that opens, select the “Pay” item.
- On the page that opens, you need to find in the “Payment for purchases and .
- In this block, you need to select a government agency whose competence includes regulation and control over certain fines and payments. You can choose: State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, Bailiff Service, Federal Tax Service, Federal Migration Service, courts and other federal services.
- If you need to pay a traffic fine, you should follow the appropriate link.
- In the page that opens, select the “Fines” field.
- In the form that opens, you must select a service: pay by receipt or find the required fine. The search can be done by entering the driver's license number or vehicle registration certificate number. If you know the receipt number, you must enter its number. After entering the number, you need to click the “Continue” button.
- If you have unpaid fines, data about each of them will appear in the “Unpaid fines” field on the page that opens.
- From the list of fines you need to select the one you plan to pay and click “Continue”.
- In the form that opens for a specific fine, you need to enter the amount to be paid in the appropriate field and continue.
- On the transaction confirmation page that opens, you need to check the correctness of the data. If everything is correct, then confirm using the code from SMS or entering a one-time password.
Fines and penalties are paid in a similar way in other government departments (Federal Bailiff Service, etc.). You need to select the appropriate department and enter the necessary personal data. For example, if payment is made to the Bailiff Service, you will need: SNILS, passport series and number and TIN.
How to pay fines in Sberbank Online: tips and tricks
Payment of fines can only be made from a card, so before starting the procedure you should make sure there are sufficient funds on it.
It is also worth knowing that payment can only be made by the person in whose name the card was issued, and to whom a fine was issued or penalties were assessed.
Otherwise, if the data does not match, the fine will not be transferred to the category of paid, and the person will remain on the list of debtors.
Regardless of the method of paying fines, it is recommended to always print out and keep a receipt confirming payment, in order to avoid misunderstandings or all kinds of errors, which, unfortunately, are not uncommon.
Today, you can take advantage of opportunities to pay traffic fines. It allows you to automatically track all fines, receive timely information about them and pay for them by sending SMS. The service can be activated in your personal account of the Sberbank Online service.
New on the site
Recent comments
The order of repayment of utility bills
Many debtors are interested in the question of the order in which debts for housing and communal services are repaid and by what rule it is established.
Thus, Article 319 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that when repaying a debt, the following sequence must be observed:
- lender costs;
- interest charges;
- amount of debt.
Based on the above, it can be assumed that when paying off debts for housing and communal services, you first need to pay a penalty, and then the principal amount. However, this approach is considered incorrect. The fact is that utility bills in most cases are costs for the management company, since it is settled with the resource-supplying organization using internal reserves.
The owner of the premises must first return the main debt for housing and communal services, and then pay a penalty.
In addition, if in any month the amount of payment for a specific utility service exceeds 25% of the amount accrued for the same period last year, then the debtor has the right to receive an installment plan. So, in this case, the monthly receipt for payment of housing and communal services will include the following components:
- payment for the current month;
- 0.083 (1/12) of the amount of existing debt;
- interest for using installment plans (refinancing rate increased by 3).
Penalty differentiation
As mentioned above, penalties for late utility payments vary depending on the legal status of the housing and communal services consumer. They will be different for management companies, individuals, legal entities, homeowners' associations and building cooperatives.
For example, for heat supply organizations, water supply and sanitation enterprises, and management companies, the fines will be as follows:
- from 1 to 60 days of late payment – 1/300 of the refinancing rate (key);
- from 61 to 90 days – 1/170 of the rate;
- from 91 days onwards – 1/130 of the Bank of Russia refinancing rate.
For legal entities not associated with the above-mentioned industries, homeowners associations, housing construction cooperatives, the penalty will be the same - 1/130 of the refinancing rate, starting from the first day.
If you have an advance payment system for housing and communal services, then the specific timing of the accrual of penalties may differ. It is best to clarify them with your service organization - management company or homeowners association.
Are rent penalties legal, and is it possible not to pay them?
Undoubtedly, charging penalties for late payments for housing and communal services is an absolutely legal way of influencing the debtor. The legislation clearly states the possibility of using such a measure. It will not be possible to remove it citing illegality of use.
At the same time, in some cases these penalties may be written off. This means that the apartment owner will no longer have to pay them.
Thus, accumulated amounts of penalties for non-payment of utilities are written off in the following main situations:
- expiration of the limitation period (3 years according to clause 1 of Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- declaring the debtor bankrupt;
- impossibility of collecting penalties within the framework of enforcement proceedings;
- death of the owner or liquidation of the organization.
In addition, in some cases, the accrued penalties may be reduced (more about this below).
Examples of calculations using the new system
For ordinary owners of apartments and private houses, the following penalty calculation schemes are relevant:
The amount of the penalty depends on the number of days when payment was not made
- For example, you owe the management company 6,000 rubles. Starting from the 31st day of late payment, you will be charged a penalty every day in the amount of 6000 * 0.11 * 1/300 = 2.2 rubles. That is, for the first three months (including the first “preferential” month) you will be charged 132 rubles in penalties.
- Starting from 91 days, the penalty rate rises to 1/130 of the rate. If we count the same 6,000 rubles, then in the fourth month you will already be credited 5.08 rubles per day. That is, for the fourth and each subsequent month you will have to pay 152.4 rubles. Thus, the penalty for a delay of six months will be almost 590 rubles. However, do not forget that you will receive new utility bills throughout these months. And if you do not pay for them, the amount of the penalty will increase significantly.
How to write off penalties for rent and utilities
The course of action to be followed depends directly on the individual circumstances of a particular situation. It is also important to have legal grounds for implementing the procedure for writing off penalties for housing and communal services.
If the principal debt is repaid
If the debtor has paid off the main “body” of his debt for utilities, then it will be easier for him to find a compromise with the management company.
In such a situation, you can take the following actions:
- Ask the management company to restructure the remaining amount of debt (in the form of unpaid penalties). In this case, an appropriate agreement is concluded between the parties, according to which the owner can be provided with an installment plan. This means that he will repay the existing debt for accrued penalties monthly in installments.
- You can file a petition with the court to reduce the amount of the fine, citing one of the following grounds:
- presence of errors in calculations for housing and communal services;
- difficult financial situation;
- other circumstances that are significant in order to reduce the amount of the penalty.
Is it possible to write off penalties on utility bills in full?
As already noted above, accrued penalties can be completely written off only in exceptional situations, when the debtor has been declared bankrupt, the statute of limitations has passed, the death of the apartment owner has occurred, or if collection cannot be implemented within the framework of enforcement proceedings.
In all other cases, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the accrued penalty. The debtor can only count on reducing its size (if there are compelling reasons for this).
Write-off of utility debt due to bankruptcy
It was already noted above that one of the ways to completely get rid of utility debt is to declare an individual bankrupt.
It is immediately worth noting that this method is quite lengthy, complex and can only be used in exceptional situations if the appropriate prerequisites are present.
In paragraph 1 of Art. 25 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that a citizen can be declared bankrupt if the court finds that he is unable to satisfy the demands of creditors, as well as fulfill his obligations to pay various bills.
In general, the bankruptcy procedure for citizens is regulated by the provisions of Chapter X of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Insolvency”. In order to resort to this option, the following basic conditions must be met (clause 2 of Article 213.3):
- the total amount of debts must exceed 500,000 rubles;
- the period of delay is at least 3 months.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 213.27 of the above-mentioned Federal Law of the Russian Federation, in case of bankruptcy, debts for housing and communal services are repaid in the third place. However, if the debtor’s property is not enough for final settlement with all creditors, then the remaining debts are written off (clause 6 of Article 213.27).
If residents have been away for a long time
It’s worth noting right away that temporary absence from an apartment is not grounds for exempting its owner from paying utility bills (this is especially true for heating bills).
At the same time, persons who were temporarily absent from the apartment have the right to submit an application to the Criminal Code for a recalculation. This is possible subject to the following conditions (clause 86 of section VIII of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 354):
- the owner of the premises stays in another place for more than 5 days in a row;
- the apartment is not equipped with an individual meter for recording consumed resources (provided that their installation is impossible for technical reasons).
As a result of the recalculation, the cost of housing and communal services for a specific period will decrease, which will accordingly reduce the amount of fines accrued for late payments.
Other options for reducing the amount of penalties
In addition to the above methods, another option for reducing the penalty accrued for housing and communal services debt is to submit a corresponding petition to the court. In this case, you can refer to the following reasons in your application:
- The management company incorrectly calculated the cost of utilities, which led to a significant increase in the amount of the penalty. Moreover, in this case, you must attach to the application your own calculation, as well as current standards and tariffs.
- Disproportionality of the accrued fine to the consequences that arose as a result of the delay. In this case, the court may decide to reduce the amount of the penalty (clause 1 of Article 333 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Difficult financial situation (loss of ability to work, lack of permanent work, etc.) - often when considering a case of non-payment of housing and communal services, the judicial authorities also take into account the family and financial status of the defendant.
What else did the new law bring?
In addition to accruing penalties, utilities may also be disconnected for non-payment.
In addition to changing the system for calculating and collecting penalties for late payment of utility services, amendments to the legislation affected another measure of punishment for violators.
As is known, in addition to penalties, resource supply organizations have the right to limit or completely stop the supply of electricity, heat, water and gas. Of course, before cutting off a consumer from an energy resource, there will be several warnings.
Usually the first action is to turn off the lights in an apartment, private house or entire building. There are often cases when, after an electrician’s visit and cutting the wires, residents are connected without permission. Such actions are a violation not only of current legislation, but also of safety regulations. Therefore, amendments to the law significantly increased penalties for such arbitrariness.
Now, if an independent connection to electrical and heating networks was recorded, the fines will be:
- for individuals – 10-15 thousand rubles (previously 3-thousand);
- for officials, the penalty increased to 30–80 thousand rubles;
- legal entities will have to pay from 100 to 200 thousand rubles for arbitrariness.
How to challenge late fees for utility bills
Sometimes in practice situations occur when the management company sets unreasonably inflated penalties for utilities that the owner of the premises did not pay on time.
If you find yourself in such an unpleasant situation, in order to challenge the decision of the representatives of the Criminal Code, you must act as follows:
- First of all, you need to request a detailed calculation, on the basis of which the total amount of penalties for the existing debt is derived.
- Having received all the necessary documents from the Criminal Code, you should carefully compare everything and make your own calculations. It is best to hire a competent specialist who can competently perform this task.
- If discrepancies are detected, the owner of the premises should write a statement to the Criminal Code stating that an error was made in the calculation of the penalty and the accrued amount must be adjusted. In this case, you should attach your own calculations to your letter.
- If representatives of the management company refuse to fulfill this requirement or completely ignore it, then the next step may be to file a corresponding statement of claim with a judicial authority.
- If the claim is satisfied, the apartment owner will not have to pay an inflated penalty. The amount will be subject to forced adjustment.
The sequence is relevant for 2019.
Types of fines and penalties that can be paid through Sberbank Online
In your Sberbank Online personal account you can pay any fines, penalties and taxes imposed by government authorities in the Russian Federation. These include:
- Fines from the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, Ministry of Internal Affairs, MADI, AMPP.
- Customs payments.
- Debts in the FSSP.
- Fees for migration actions.
- Payments to Rosreestr.
- Fees on the State Services service.
- Taxes and penalties.
- Fines in the Pension Fund, etc.
- Payments to courts, etc.
A complete list of fines and penalties accepted for payment can be found in the section “Staff Police, Taxes, Fines”. If you do not find the organization you need in the list, you can use the search and enter the name.
If the user wants to check the presence of overdue tax debts, he must go to the “Search and payment of taxes by the Federal Tax Service” tab, and then select the search section by TIN.
When specifying the TIN, only those debts that were not repaid within the period specified in the notification will be reflected.
To pay fines, taxes and penalties through Sberbank Online, you must register in the remote service. Only holders of Sberbank cards with a connected Mobile Bank can obtain credentials for authorization in their personal account.
You can find out your account details at a Sberbank branch or ATM. When logging in for the first time, the system will prompt you to change the password to a different combination. If you install a mobile application, you must generate a five-digit code for subsequent authorizations.
Payment of penalties and fines through Sberbank Online: step-by-step instructions
You can pay taxes and penalties through your Sberbank Online personal account within a few minutes. To do this, the user needs to follow the algorithm:
- log in to the system;
- go to the “Payments and Transfers” section;
- Among the available types of payments, select the “Traffic Police, taxes, fines” tab;
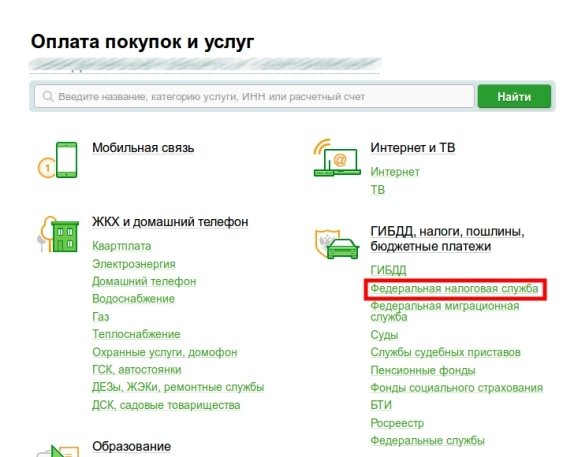
- find the subsection “Search and payment of taxes to the Federal Tax Service”;
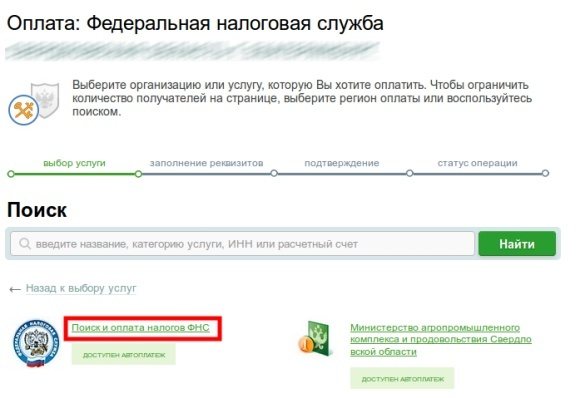
- if you have a receipt for payment of taxes and penalties, select the payment item by document index;
- if there is no receipt, or you are not sure whether there is a debt, go to the tax search section by TIN;
- after entering the TIN or zip code, you need to select the card from which the payment will be debited;
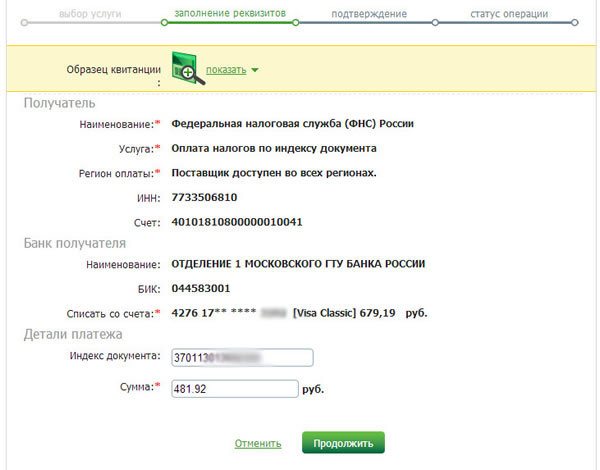
- press the “Next” button and check again that the entered data is correct;
- The next step is to confirm the operation with an SMS code. The password will be sent to the mobile number linked to the card.
After making the payment, you can save and print the receipt. Even if you haven't printed the receipt, you can find the payment in your transaction history at any time and save the receipt.
Important! Check the amount of funds in your card account. If there is not enough money, the system will reject the payment.
Commission for payment of taxes and penalties is not withheld. Funds can be written off free of charge from any Sberbank debit or credit card.
The Sberbank Online service allows you not only to pay taxes and penalties, but also to find out up-to-date information on overdue debts. If desired, the client can request information about the presence of debts on the website or at the Federal Tax Service branch.
When paying contributions to the FSSP, after the “Payments and Transfers” section, you need to select the “Bailiff Service” item. If you have a receipt on hand, select the appropriate item. To clarify the presence of debt, select the search tab and enter the SNILS number, series and number of the passport and TIN.
Useful tips
Taxes in Russia must be paid on any income of an individual. When calculating wages, the employer independently makes contributions to the Federal Tax Service. Moreover, if a citizen rents out real estate or transport, it is also necessary to pay an annual contribution to the tax service.
Taxes are also assessed on property owned by a person. This could be an apartment, a country house or a car. Any winnings, prizes, deposits relate to the additional income of citizens, so the state withholds part of the payment.
Unpaid taxes on time can become an obstacle to obtaining a cash loan or traveling abroad. Cases often arise when bank accounts and cards are seized from persistent defaulters. To avoid getting into an unpleasant situation, do not put off paying fines and taxes.
Penalties are charged on overdue debts. As a result, a person overpays due to late payments.
You can check the presence of accumulated debts on the websites of government agencies: the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Tax Service, the Federal Bailiff Service, etc. The Sberbank Online service has access to the databases of many budget organizations, so you can find out the amount of current debts in the client’s personal account.
To pay off traffic police fines, you can set up the “Autopayment” function, which will help you track recent fines and pay them off instantly. The service is activated in the settings of your personal account.
The payment processing time often does not exceed one day. If technical failures occur, repayment may be delayed up to 5 days.
Thus, Sberbank card holders can easily pay off any fines, taxes and penalties. This can be done through ATMs and terminals or via the Internet. Sberbank Online will help you make a payment for another user; you only need the necessary details.
It is advisable to save and print receipts of completed transactions. In this case, you will always be able to prove the fact of payment, and you will not have to look for the required payment in the service history. If you encounter difficulties when making a payment, you can call the Sberbank hotline and ask questions that interest you.
Source: https://bankiinfo.com/sberbank/oplata/peni-po-nalogam-cherez-sberbank-onlajn.html
Application for a reduction in penalties for utilities
If the owner of the premises is already being investigated for debt collection, he has the right to apply to the court with a petition to reduce the amount of the accrued fine.
A sample of such a document includes the following main points:
- “Head” of the document - information about the judicial authority (name), the plaintiff (name of the management company) and the defendant, who is the applicant (full name of the debtor, telephone or email address), is consistently reflected here.
Immediately after the “header” in the middle of the sheet, the full name of the document is indicated. It may look like this: “A petition to the court to reduce the amount of the penalty.”
- Introductory part - the following general information regarding the trial is stated here:
- name of the court;
- details of the civil case;
- name of the plaintiff (CC);
- name of the defendant (debtor);
- subject of dispute.
- A request to reduce the penalty with the obligatory indication of the grounds on which it is put forward (disproportionately large amount, difficult financial situation, error in calculations, etc.). You must also provide a link to the relevant provision of law.
Additional documents are attached to the completed application (for example, a self-made calculation of the penalty), the applicant’s full name is written again, and then his signature and date are affixed.
Is it legal to charge penalties on the amount of debt for housing and communal services after a court decision?
The decision to reduce the amount of the accrued penalty is not a basis for its complete cancellation. The debtor must pay the assigned penalty until the existing debt on utility bills is fully repaid.
The situation is completely different when it comes to the expired statute of limitations or the bankruptcy of the apartment owner. If there is an appropriate court decision, the management company will be obliged to write off the existing debt for housing and communal services, including the accrued penalty.
To summarize the above, it should be noted that the accrual of fines is an inevitable punishment for late payments for utility services. In the absence of certain circumstances, the owner of the apartment will be forced to pay this amount. However, in some cases, its size can be reduced or even canceled (write-off procedure).
Requirements for an online cash register receipt
To a frequently asked question from entrepreneurs: “Is it necessary to indicate the name of the product in an online cash register receipt?” It is worth noting that the legislation establishes certain benefits in terms of generating receipts at online cash registers for stores operating under the following tax systems:
Federal Law No. 54 allows you to include other details in the check - based on the characteristics of the specific sphere of economic activity of the business entity. For example, this could be the organization’s logo, information about certain promotions, or other information useful to the buyer.
This is interesting: If during a divorce one of the spouses does not agree to sell the jointly owned house
Penalties for non-payment of loans
Penalties are a constant companion for those who do not fulfill their obligations under loan agreements. But if previously banks themselves regulated the amount of penalties, now at the legislative level all penalties are limited.
This was done on purpose, since some creditors set unreasonably high penalties, plus fines. As a result, borrowers who committed even a one-time delay fell into a real debt hole from which they could not get out.
So situations arose when, with an initial loan amount of 100,000 rubles, a person found himself owing 1,000,000 rubles or even more. To stop this, the Central Bank decided to limit bankers in terms of assigning penalties, which is reflected in Federal Law No. 353 On consumer credit.
Financial institutions are offered a choice of two options for calculating penalties:
- If the interest due under the agreement continues to accrue. In this case, penalties will be 20% per annum.
- If the bank stops accruing interest, then the penalty amount is 0.1% per day.
In the vast majority of cases, banks adhere to the scheme of calculating penalties in the amount of 20% per annum and at the same time continue to assign interest under the agreement. The law prohibits them from taking fines.
If you do the calculation, then 20% per annum is not so much, only 0.055% per day. For example, if the amount overdue is 10,000 rubles, then the next day it will be credited with 5.5 rubles. But these 5.5 are counted towards the unpaid amount; the next day the penalty will be calculated from 10,005.5 rubles.
If you are in arrears on your loan, it is better not to delay, but to turn to the bank for help, for example, for restructuring. Otherwise, next month, after the next payment is not made, the overdue amount will increase and the penalties will be higher. And the further, the more serious the growth of debt will be.
Penalties for loans from microfinance organizations
A slightly different situation concerns those who owe money to microfinance organizations. The penalty for the amount of debt is calculated exactly the same as in the case of a bank loan. That is, according to Federal Law-353, this is 20% per annum, plus the rate stipulated by the contract.
But it was the microcredit sector that drove borrowers into real bondage. The fact is that today the marginal rate on loans is 1% per day, which is most often prescribed by lenders, and this is 365% per annum. That is, 365% is added to 20% per annum. As a result, the debt increases dramatically quickly.
In order to protect borrowers from unreasonably high penalties, the amount that microlenders can demand in the form of penalties is legally limited. In the form of penalties and interest, the MFO is not authorized to demand from the borrower more than 1.5 times the loan amount.
Simply put, if the amount of microloans at the time of issuance was 10,000 rubles, then in the form of interest and penalties in case of delay, the microfinance organization can charge a maximum of 15,000. That is, the total amount required for repayment cannot be more than 25,000 rubles.

All legal MFOs comply with this legal norm. All companies are controlled by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, so it is not in their interests to exceed their powers.