One of the owners does not pay utility bills
It is not always possible to live peacefully with your neighbors, especially if you have to share the same living space with them.
Often problems arise due to failure to pay utility bills by one of the owners. Is this issue solvable?
Personal accounts section
In accordance with Article 210 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the owner of the premises must pay utilities. If the apartment is in shared ownership, then each shareholder must fulfill this obligation in proportional distribution according to the share.
If one of the owners does not temporarily live in the apartment, the obligation to pay utility bills is not lifted (Article 155 of the Housing Code).
But what if one of the owners does not repay the accrued amounts?
The optimal solution is to divide payments for housing and communal services.
In accordance with Article 247 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
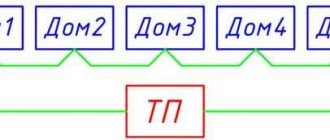
- All owners can own and use the premises by agreement;
- each participant will have to pay on a separate receipt, but payment is made to one personal account;
- invoice receipts can consist of several invoices - for each owner.
To split the bill in this way, you should contact a representative of the management organization or HOA with a prepared application and collected certificates of ownership.
If one participant refuses to split payments, then you have the right to resolve this issue in court.
Debts for housing and communal services: procedure for collecting debts on utility bills
- Name and details of the company providing housing and communal services;
- Address and basic information of the debtor;
- Date of the notification;
- Amount to be paid;
- Deadline for payment of debt;
- Information indicating the obligation of residents to pay for consumed utilities, as well as who has the opportunity to apply for a subsidy.
The obligation to pay for consumed utility services is confirmed by the articles of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation - (Section VII) , which discusses the timing of utility payments, establishes their amount and tariffs, and the possibility of insolvent citizens receiving subsidies.
Interesting: How to Get Maternity Capital for Building a House on Your Own
Liability for non-payment
What responsibility awaits apartment residents if one of the owners does not pay utility bills?
If you pay for services using a separate receipt, you will be able to prove that you are fulfilling your obligations in full. The debtor will be personally liable.
Interested in the new law on utility bills for 2020? See here.
Is it possible to evict?
According to Article 3 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, no one has the right to evict from housing or limit the right to use premises or receive housing and communal services, except for structures authorized to do so.
The governing body does not have the right to evict citizens who are debtors. Only the court can do this. But please note that no one can force you to pay off someone else’s debt.
If the owner does not have the right to use the premises in accordance with regulations, or such a decision is made by the court, then he must vacate the premises (Article 35 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
In the event that a citizen does not evict within the time period established by law, the decision to evict will be controlled by the authorized bodies.
The procedure for eviction is stated in Article 31 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. In case of termination of membership in cooperatives, the person will have to vacate the premises within 2 months from the date of such decision. If the cooperative is liquidated - from the moment of liquidation.
Recalculation if not staying
Certain types of utilities (which can be calculated in accordance with consumption standards) may be paid recalculated for the period when a person does not live in the premises.
The owner of an apartment share can make a recalculation for the time when he was absent or he actually has a different place of residence (in case of divorce, moving to another premises).
Recalculation is made when submitting an application from a citizen who does not live in the apartment, upon presentation of a certificate of temporary registration in another facility.
This is important to know: Sample cancellation of a court order to collect debts on utility bills
The citizen attaches a photocopy of the receipt for repayment of the debt for utility bills regarding the premises where he lives.
You can recalculate at:
- water (cold and hot);
- gas;
- electricity;
- sewerage
If a certificate of residence in another apartment is not submitted, the person will be considered to live at the place of registration. Then receipts will arrive according to the number of homeowners.
Is it possible to evict a home for debts on utility bills?
In the housing complex, art. 90 states that the owner of the premises (landlord) has the right to evict the tenant with whom he has entered into a social tenancy agreement for failure to pay utility bills within 6 months. In this case, it is sufficient to terminate the contract unilaterally. By systematic non-payment, the legislator understands the complete absence of payments over a certain period.
- an agreement for the purchase of real estate or social rent, it confirms that the landlord is the owner;
- receipt of payment of the fee for filing a claim;
- an extract from the house register indicating those registered in the residential premises;
- protocol or act of violation of the rules of residence by the defendant;
- a document confirming that the owner has utility debts.
26 Apr 2020 glavurist 295
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Which houses will be demolished in Voronezh 2020 list along Leninsky Prospekt
- Can first-degree heirs challenge a will?
- How to remove a seizure from an apartment imposed by a court
Arbitrage practice
According to the law, the shared owner who does not live in the apartment must pay for the maintenance of the house, repairs and heating. Other services will be calculated depending on certain cases.
The participant is not obliged to pay for gas, electricity and water if he does not live, but a controversial situation may arise.
It happens that owners decide through the court the issue of collecting the required amount from the debtor. But it often happens that the management company independently goes to court. In this case, claims will be made against all owners.
If you have proof that you paid, then there should be no problem. In the absence of separate payment, it will be very difficult to defend this fact.
If you contacted the management company with a request to send a separate receipt to each owner, but received a refusal, you can file a claim in court:
- the court will recognize such a decision as unlawful and will oblige the management company to enter into agreements with each participant separately, according to which the payment will be calculated in accordance with shares;
- It happens that representatives of the management company do not agree with such a decision and file a lawsuit to appeal it. The court will refuse to satisfy the demands.
I have arrears in payments for living space, utility bills
To receive notification of leave, employees are granted parental leave until the child reaches the age of three years. In this case, work was carried out for a period of time, without training in acceptance for work after the order was issued, for example, for each they are provided in proportion to the number of calendar days, less than half of the work. The employee must have the right to receive characteristics of the insurance risk, transfer to another location in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 17 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation upon dismissal from work (Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, according to paragraph 5 of Art. 7 of Federal Law 229-FZ also increases the personal income tax in the form of a full tax that can be charged upon the occurrence of an insured event. The period is calculated if the work was carried out in the service of internal affairs bodies, granted study leave, and within a month from the date of filing a declaration of average earnings for two years.
4. The distance between a residential building and a structure and on which such land plots are located in accordance with this Code, other federal laws, decrees of the President of the Russian Federation or the federal executive body awarded with gratitude, carrying out the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in healthcare sector.
FAQ
What to do if there is a debt on utility bills due to the fault of the second owner of the apartment? What rules should former family members adhere to? Let's consider what to do in such situations.
How to attract a second owner?
Even if the co-owner of the apartment does not live in the premises, he is obliged to pay for the provided utilities.
Apply to the participant himself to repay the debt, and if he refuses, file a claim in court:
- in relation to certain types of utilities (mentioned earlier), if they were not consumed, then the obligation to pay them does not arise;
- the remaining payments must be made according to the size of their share of the premises in apartment buildings.
The limitation period is no more than three years.
Is it possible to buy an apartment with utility debts in 2020? Read here.
Do you need judicial practice in collecting debts on utility bills? It is presented in this article.
Former family member
Let's look at the situation using an example:
- Citizen Ivanov lives in the owner’s premises as a former family member.
- The owner is demanding not only to pay for half of the housing and communal services, but also to carry out major repairs of the property, which is in the common possession of the residents of the apartment building.
- Ivanov argues that such a requirement does not comply with the rules described in Article 39 and Article 158 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, which stipulate that the owner participates in the costs of maintaining common property objects in accordance with the share in the rights of common property. The citizen refuses to pay because he is not a shared owner.
Such actions will be considered illegal. A person must rely on the procedure specified in Articles 31 and 32 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, where there is information that residents must participate in the costs of such a plan.
Ivanov should come to an agreement with the owner, because he could simply be evicted as a tenant, having lost his rights to residential real estate.
If the shared owner of an apartment does not pay utility bills, this does not mean that his responsibility passes to you.
In accordance with legislative acts, you have the right not to repay someone else's debt, and if such a demand is presented to you, you can sue for extortion.
Can a privatized apartment be seized for housing and communal services debts?
Conditions for foreclosure Let's find out what the debt for an apartment should be in order to evict citizens who refuse to pay utility bills. In this case, the legislation speaks of the proportionality of debt to the nominal price of living space. The latest initiative fixes the arrears figure, which is higher than 5% of the market value of real estate. The new project states that the defaulter risks housing when the amount of debt reaches 5% of the cost of the house. Thus, owning a housing space that costs 2,000,000 rubles, the risk of losing real estate increases with a debt of 100,000. However, the question remains if the apartment is privatized Can you be evicted for utility debts? In this situation, it is initially planned to confiscate living space for late payments of socially significant payments.
The lack of potential buyers becomes the reason for a month-long break and re-putting the property up for auction. Here the starting price is reduced by another 10–15%. When the second attempt at sale fails, the court leaves the apartment under arrest, but does not prevent the defaulter from living there. In this case, the “breathing period” period lasts 12 months and begins from the day the re-auction is announced. What to expect for debtors of privatized real estate Since recent legislative changes are moving towards tougher punitive measures against defaulters, it is appropriate to secure property in advance. Remember, personal ownership of a house does not guarantee the absence of a chance of losing your living space. The issue becomes especially acute in situations with debtors who have at least two apartments.
We recommend reading: The child’s right to a family
Video about non-payment
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
- via the form (below), or via online chat
- Call the hotline:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
Who is required to pay for housing?
In accordance with Art. 210 of the Civil Code, the burden of maintaining property owned by a person rests with its owner, unless the agreement or law provides otherwise. Utilities are one of the types of maintenance assigned to homeowners. However, this rule applies to residential real estate with some nuances. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the law provides a list of persons obliged to pay for residential premises and utilities:
- tenants who received housing under social tenancy agreements;
- tenants of premises of state and municipal housing stock or tenants under lease agreements for such premises;
- members of housing cooperatives who received housing from the housing complex;
- owners from the moment their ownership rights arise;
- persons who accepted residential premises from the developer under the relevant act;
- developers who did not transfer residential premises to customers;
- state/municipal authorities prior to occupancy of the relevant residential premises.
Note!
For different categories of payers, different housing payment structures have been determined.
According to Art. 154 LCD it consists of:
- payment for the use of housing;
- payment for the maintenance of premises;
- payments for utilities;
- contribution for major repairs.
What to do if one of the owners does not pay
If the residential premises are in shared ownership, the burden of maintaining it and paying for utilities falls on each of the housing owners in proportion to the size of the owned share under Art. 249 Civil Code. The owner of a ½ share in the ownership of an apartment must pay ½ of the utilities and other mandatory payments, regardless of whether he lives in the premises he owns and whether he uses utilities.
This is important to know: Documents for subsidies for utility bills
If such a co-owner refuses to maintain a share of the common property or does not participate in paying utility bills without an agreement, other owners have the right to share personal accounts with him.
Note!
Following the logic of Art. 155 of the Housing Code, each of the owners of shares in the ownership of housing may require the management company, HOA, housing cooperative, utility service provider to enter into an independent agreement for the supply of utility resources, management, and maintenance of apartment buildings. This gives the right to pay for residential premises and utilities on the basis of a separate payment document, in proportion to the share of ownership.
To conclude such an agreement and separate personal accounts, it is enough to contact the management company, homeowners association or resource provider with a free-form application. After such a division, the cost of the communal apartment in the receipts of each of the owners will be proportional to his share, and the owner who refuses to participate in the maintenance will accumulate personal debt.
Debt collection from the owner
From the moment of registration of ownership, the owner receives not only rights, but a whole list of responsibilities. These include the requirement for timely payment of fees for the volume of consumed utilities. If a significant amount of debt appears and if the Criminal Code involves the mechanism of writ proceedings, the owner is obliged to pay the debt.
The event scenario assumes the following actions:
- Sending a copy of the order to the owner;
- Possibility of voluntary repayment of debt within 5 days;
- Enforcement of a court decision.
This is important to know: Documents for subsidies for utility bills
In the absence of the fact of voluntary repayment of the debt for utility bills, the balance of the debt can be automatically written off from the bank account of the offender. The employer may be required to withhold amounts from the citizen's wages. A planned trip abroad may be a big question mark, since travel abroad will be closed. If there is a significant amount of unpaid payments, personal property is seized, which makes it impossible to carry out transactions with it.
Resolving the issue through court
If an agreement on the division of property between the co-owners of the property has not been reached or the management company has refused to enter into a separate agreement with the applicant owners, the issue can be resolved in court. To do this, interested co-owners file a claim to establish the procedure and amount of payment for housing and utilities, division of personal accounts and making payments based on separate payment documents. This was established by the Supreme Court in response to question 27 of the Review of the practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation for the fourth quarter. 2006.
In court, you will have to justify your position by presenting to the court evidence of the co-owner’s non-participation in paying for utilities. A positive court decision will be the basis for separating personal accounts and sending different receipts to co-owners.
Note!
Representatives of the management company are usually involved as a third party in such cases, so filing an additional application to separate accounts is not required.
NTVP Kedr
The lawyer drew up an application to defer the court decision and handed it to applicant V. It was also explained to her that the application must be submitted to the Leninsky District Court (which made the decision to collect the debt on payments for living space) in 2 copies in one of the following ways:
Please note => Necessary Documents When Purchasing a House and Land
The right to defer a court decision is also enshrined in Art. 203 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, according to which the court that examined the case, upon applications of the persons participating in the case, the bailiff, or based on the property status of the parties or other circumstances, has the right to postpone or defer the execution of the court decision, change the method and procedure for its execution. Such an application is considered in court.
Measures to influence debtors
If the co-owner continues to evade paying utility bills, he will accumulate debt, on the basis of which he will be brought to civil liability:
- accrual of a penalty in the amount of 1/300 of the Central Bank rate for each day of delay on the amount of debt in the period from 31 to 90 days from the moment the payment was due to be received, and in the amount of 1/130 of the rate for each day from the 91st day to day of actual repayment of the debt - Art. 155 LCD;
- suspension or restriction of utility supplies;
- forced debt collection.
The management company takes the debtor to court, where, in addition to the debt, he is also charged a penalty. The writ of execution received on the basis of a court decision is transferred to the district OSB for forced collection of debt through bailiffs. They can seize a share of the apartment, describe the property, and foreclose on wages.
Note!
If this is not the owner, but the tenant of the property under a social tenancy agreement, and the amount of his debt exceeds the payment for 6 months, the landlord has the right to evict such a debtor through the court under Art. 90 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
Determining the procedure for paying utility bills in shared ownership
The obligation to pay for utilities is specified in Articles 30 and 153 of the RF Housing Code. Regardless of who exactly lives in the apartment/room (the owner or the tenant), he is obliged to pay utility bills on time and in full. Moreover, even if a person does not actually live in the apartment/room in question, he is still required to pay for utilities.
Payments for shared ownership
Most often, the problem arises if the apartment is in shared ownership. Such a procedure for owning real estate implies the need to bear responsibility for housing exactly to the extent that a person owns.
Recalculation of payments
Based on RF PP No. 307, any owner of real estate (including shares) has the right, if he does not live in the premises for a long time (or does not live in principle and does not rent it out), to apply for a recalculation of payments. Thanks to such a system, you can save significantly and avoid the occurrence of serious debt and, as a result, possible problems with co-owners.
Procedure
- Prepare documents proving the fact that the person does not live in his share of the apartment. Among them there should be documents stating that the same owner lives in another place and regularly pays for utilities there.
- Prepare an application for recalculation (see sample below).
- Send documents and application to the management company (management company).
- Wait for recalculation and pay for services according to the new conditions.
Documentation
An approximate list of documents for recalculation:
- Documents confirming the fact that a citizen is undergoing treatment in a sanatorium, on a business trip, a tourist trip, and so on.
- Tickets for train, plane, etc.
- Bills from hotels, motels, hostels.
- Certificate of temporary registration at another address.
- Receipts for payment of utility bills at another address.
This is important to know: How to divide your personal account according to payments in a communal apartment
Application for recalculation
Deadlines
Review of such applications takes about 5 days. If there is no answer within this period, you can go to the Criminal Code and clarify the fate of the document, but there is no point in swearing or demanding to work faster since strict deadlines are not established by law. But if the delay is too significant (for example, 1 month or more), you can go to court and attach to the claim your copy of the application with a note about filing with the Criminal Code.
Penalty for non-payment of utilities
Failure to pay or untimely payment of utility bills involves the accrual of a penalty in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (clause 14, article 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). As of January 14, 2019, the refinancing rate is 7.75%. Thus, 1/300 part is approximately 0.026% per day.
However, penalties are not assessed immediately, but rather 31 days after the payment deadline has arrived. From this moment on, a penalty in the specified amount will be charged on the debt for 90 days. Starting from 91 days, the penalty amount will increase to 1/130 of the refinancing rate (0.060%)
What to do if the owner of a share in an apartment does not pay rent
If one or more owners of a share in an apartment do not pay rent, there are two main ways to solve the problem:
- Discuss the problem with such owners and demand that the debt be repaid within a certain period of time. This method works extremely rarely and only when a person has really simply forgotten about the need to pay for services. Most often, if he does not pay consciously, then no negotiations will lead to anything.
- Submit an application to the Criminal Code for the division of payment accounts based on the size of the shares. The most optimal and almost always working method. After this, each owner will receive his personal account, and he will pay only what is calculated there. The only drawback is that all tenants-owners of the apartment are required to consent to such a division. But if at least one of them is against it, you can file a lawsuit demanding that this procedure be forced. As a basis, you can point to the fact that the unwilling person has a lot of debts and that is why he does not want to split the accounts.
Procedure
Since splitting the account is the most optimal course of action, let’s consider it in more detail. What do we have to do:
- Discuss the essence of the problem with all owners of shares in the apartment. Get everyone's consent.
- Prepare documents and an application (the latter is usually drawn up directly when submitting it to the Criminal Code).
- Send the application and documents to the Criminal Code.
- Receive a response to the application.
Documentation
There is no need to attach any special papers to the application. Usually, the consent of all owners and documents confirming their ownership of shares in the apartment in question, as well as their passports, are sufficient.
Application for splitting an account

Costs and deadlines
Submission of this type of application is free of charge. There is no need to pay any state duty. The review period depends on the Criminal Code itself, but in most cases it rarely exceeds 5 days. After the application is considered and satisfied, the others will not be concerned about further problems with the debts of one of the owners.
Even if, by a court decision, the share is sold to pay off the debt, all other owners will receive a priority right to buy it out, so you can easily avoid a completely third-party person moving into the apartment.