Why does the law on capital repairs of apartment buildings still cause a storm of negativity from the population? Let's try to figure it out. Until a certain point, major repairs of apartment buildings were carried out at state expense, since for a long time it was believed that it was not expensive for the state to maintain common property. In 2012, amendments were made to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and Federal Law No. 271 was adopted, as a result, all responsibility for major repairs of common property fell on apartment owners.
Changes in legislation
What is the essence of the amendments made to the Housing Code? Until this moment, the regulations on major repairs of apartment buildings did not regulate the rules for payment by owners of common property. At the moment, the procedure is approved by law, and its violation may be punishable. Thus, residents were required to form a cash fund from which funds would be used to restore the building.
The approved resolution makes it impossible to refuse to pay the accrued tariff. The only thing that an apartment owner can do is not to accumulate debts for a new type of utility payments if he does not fall into a preferential category, since arrest and confiscation of property can be a measure to curb irresponsibility.
Issues regarding the formation of the tariff schedule were left to the regional authorities, so payments in different regions differ greatly from each other. The amount is calculated depending on the area of the apartment: the square footage is multiplied by the minimum tariff established in the region and a monthly fee is received. It must be contributed to create a resource for maintaining the housing stock in optimal condition for full operation. At the same time, co-owners of common property have the right to increase contributions based on the minimum established in the region of residence.
A positive aspect of this reform was the emergence of more precise formulations that relate to the distribution of financial resources, the formation of tariffs, the list of activities that fall into the category of major repairs, liability for debts, and the main responsibilities of owners of common property. Perhaps in 2020, minor changes will be made to the law on mandatory capital repairs of apartment buildings, and, most likely, they will not affect the formation of the tariff schedule and the procedure by which payments are made.
Payment
With the entry into force of the document, Article 169 of the Housing Code obligated residents of apartment buildings to make deductions for major repairs (whether such fees for major repairs are legal or not from the point of view of the law, we discuss in this article).
Some differences are allowed in the implementation of the bill. The timing, range of overhaul services and other details may vary depending on the specific region.
The amount of deductions also varies greatly; for example, in Moscow it is higher than in other regions of the Russian Federation.
A certain freedom is also provided in terms of choosing the method of accumulating contributions. Owners have the right to decide which of the two methods is most preferable. A decision requires a two-thirds vote. The first option is that the funds are transferred to a separate bank account. The second method is that the money will be transferred to the account of the state operator. The list of operators is approved at the regional level.
Credit organizations in whose accounts deductions can be stored are established by the Bank of Russia on a quarterly basis. Requirements for banks are regulated by Federal Law N271, its 176th article. In particular, the organization is subject to high capital requirements - it must be at least 20 billion rubles.
There are many negative opinions and criticism regarding the provision for major renovations of an apartment building. But as you can easily see, the bill has great flexibility. This allows you to adapt it to the needs and requirements of regions and even individual houses.
Elderly persons are provided with benefits. According to the law on payment for major repairs, owners over 80 years of age are exempt from paying contributions in full. Persons over 70 years of age are required to pay only ½ of the established amount. Benefits can also be used by such population groups as WWII veterans and disabled people.
At the moment there is no law on the abolition of fees for major repairs. Therefore, without permission, without good reason, residents do not have the right to ignore the law on contributions for capital repairs of apartment buildings. Parts 14 and 14.1 of Article 155 of the Housing Code establish late fees (penalties).
If you simply ignore the instructions, you will end up paying even more.
In addition, the law on fees for capital repairs of apartment buildings exempts residents whose house breakdown rate is 70% or more, as well as houses subject to demolition.
The situation will be similar if the territory of the house will be seized in the near future for state or municipal needs.
In this case, according to the decree of the President (Medvedev) on paying for capital repairs of apartment buildings, residents are also exempt from these payments.
In separate publications, our experts examine in more detail the legislative framework regulating major repairs. From them you can find out whether contributions for major repairs were declared illegal by the Prosecutor General's Office and the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, whether it is possible not to pay such contributions in court, and also what the decisions of the Government, the Supreme Court and the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation say regarding major repairs.
The main responsibilities of residents of high-rise buildings
Federal Law No. 271 formulates the obligations and some rights of owners of an apartment building:
- owners of parts of the common property of apartment buildings are charged with mandatory cash expenses for the maintenance of their own and common premises, the amount of such expenses is formed depending on the share that is in the possession of the owner;
- Owners of multi-apartment housing can increase the established tariffs by concluding an agreement if they jointly decide on an extraordinary event or the need for other major repairs;
- for the information of future owners of square meters: when purchasing real estate, you should know that the rights and obligations of the previous owner are transferred to the new owner, including unpaid debts under this item of expenses;
- To finance the restoration, modernization or replacement of parts of communications, the owners of an apartment building can create their own account or, by concluding an agreement, pay a special regional operator, whose responsibilities are to form a regional fund of funds.
By choice or other reasons, more than 85% of the country's population voluntarily deposit money into the accounts of large companies, the so-called regional operators. Formally, such an organization can determine the priority and distribute funds intended for major repairs. In this case, it is unknown when the turn may come to your common property. Although regional plans are created on the basis of technical monitoring of the condition of residential buildings.
It should be taken into account that the plans do not automatically include buildings that are worn out by more than 70%, and private property guaranteed by the developer. In fact, the winner from such a distribution is the old housing stock, which cannot be restored with the efforts and resources of the residents, or it will take a large amount of time to accumulate the necessary resources. Which, taking into account the rate of inflation, are becoming more and more depreciated.
Residents of new buildings are losing: at their expense, old buildings are being restored, work is being carried out that new buildings, for objective reasons, do not need and will not need for a long time. However, according to the Federal Law on major repairs of apartment buildings, everyone must pay.
What you need to know
Before changes in the official text of housing legislation in 2012, major repairs of residential buildings were carried out at the expense of the housing and communal services fund.
At the moment, this fund only provides for the relocation of residents from housing recognized as unsafe or dilapidated, if necessary.
Major repairs are now paid for by the owners of the premises. This measure, according to the legislator, will allow the residents of the building and the management company to accumulate funds for major repairs of the building.
In this case, planned or routine repairs are paid separately. In practice, many residents were unhappy with this measure
The fact is that in most houses major repairs are scheduled after a fairly long period of time.
Owners are not sure that the funds they pay may ultimately not be used for their intended purpose.
Citizens in our country are distrustful of long-term programs. It is not yet clear how the program will perform further.
It will be possible to evaluate its effectiveness a little later, when major repairs have been carried out in a significant number of houses.
Necessary information
At the moment, owners have access to the following options for forming a fund of funds aimed at carrying out major repairs:
- The funds will be transferred to a special account at home.
- Funds will be transferred to the account of the regional operator.
If the first method was chosen, then the following issues must be resolved at the general meeting:
- The amount of contribution that residents will be required to pay each month.
- Who will be the owner of the relevant account.
- The organization where you plan to open this account.
- The timing of when such repairs are expected to be carried out.
As a rule, the time frame for carrying out repair work is significant. Some houses are planned to be renovated in two or three decades. Everything will depend on the decisions of the residents and the condition of the residential building.
Effect of the regulatory framework
Until 2012, major repairs were carried out using funds from the housing and communal services fund. However, with the entry into force of Federal Law dated December 25, 2012 N 271-FZ, which introduced some changes to legal acts, in particular to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, it is carried out according to new rules.
Major repairs are carried out at the expense of the tenant. The law on the fund for capital repairs of apartment buildings applies to all apartment buildings in which there is common property
Its effect cannot be extended to owners of private households, since they have the right to carry out all repair and reconstruction actions in accordance with their own will and other existing legal acts.
About sanctions for non-payment
The consequences of non-payment are provided for in Art. 155 of the law, namely:
- payment to the capital repair fund of an apartment building is made according to the same scheme as other utility payments, within the time limits established by the meeting of owners of the high-rise building or other authorized bodies;
- Payment can be made in any way: either by transfer to the electronic accounts of the organization (operator or MKD’s own account), or by payment at any bank branches that accept such payments;
- deferment of payment is possible if information on the current flow of funds was not posted on the website of the company accepting payments from the public on time;
- if the citizen is not the owner of the residential premises, he transfers rent and other agreed payments to the owner;
- if the owner of the apartment does not live in it, he is obliged to pay regularly, as well as utility bills;
- after 30 days of overdue payment on bills, a penalty begins to accrue, at first minimal, then its rate increases (after 3 months of debt).
Read also: Compliance with licensing requirements for management companies in the housing and communal services sector
So the question of whether the accrual of penalties is legal is irrelevant, since its size, interest rate and the time after which it will begin to accrue on the accumulated debt are stipulated in Federal Law No. 271. In addition, the debt falls under the articles of the law, which indicate the possibility seizure and confiscation of property belonging to the debtor for non-payment.
Law on capital repairs
14. Persons who have lately and (or) not fully paid for housing and utilities are required to pay the creditor a penalty in the amount of one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, effective on the day of actual payment, of the amount not paid on time for each day delay starting from the thirty-first day following the day of the established payment due date, until the day of actual payment made within ninety calendar days from the date of the established payment due date, or until the expiration of ninety calendar days after the date of the established payment due date, if within a ninety-day period payment has not been made. Starting from the ninety-first day following the day of the established payment deadline until the day of actual payment, penalties are paid in the amount of one hundred and thirtieth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, effective on the day of actual payment, of the amount not paid on time for each day of delay. An increase in the amounts of penalties established by this part is not allowed.
Interesting: Lifetime maintenance agreement with dependents sample completed
About benefits
The categories of beneficiaries who are exempt from paying this type of utility bills are very few. Who has the right not to pay? First of all, residents of damaged real estate that is not subject to major repairs are exempt from such payments. Citizens living in territory that will eventually become the property of the state or municipality, or those who are tenants of such property, are exempt from payments, unless the lease agreement specifically stipulates this clause.
Based on Law No. 169 on major repairs, 50% benefits are provided for pensioners who are over 70 years old, and for those over 80 - 100%. This is all about benefits established and fixed at the federal level. Regional authorities form their own lists of beneficiaries; this category includes:
- disabled people and veterans of military operations and WWII;
- liquidators of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and their families;
- rehabilitated victims of political repression;
- large, low-income families;
- disabled people.
And some other categories of citizens. Nuances and details can be found in local governments or the social welfare service at your place of residence.
What benefits are provided by this regulatory act for services?
Some categories of citizens have the right not to pay for major repairs of buildings. These include:
- disabled people and citizens raising disabled children;
- large families;
- low-income citizens;
- citizens taking part in the elimination of man-made disasters;
- WWII participants and veterans;
- pensioners over 70 years of age.
For all categories, a payment of 50% of the total accrued amount is provided.
This is important to know: How to return 13 percent from the purchase of an apartment
List of works according to the law

Some clauses of the law quite clearly regulate the list of works, services and activities that fall under the category of “major repairs of a building”. Until this point, lawyers in the process of litigation were often faced with vague concepts of capital and current restoration of a house.
What is a capital repair program and what is the legally approved list of activities? The Urban Planning Code formulates the definition of capital repairs as follows: “a series of activities aimed at restoring and replacing main parts and structures.” The following list of repair work objects is regulated:
- main elements of the roof, roofing of the building;
- elevator facilities of apartment buildings;
- base (foundation) and facade of the building;
- engineering communications of the house;
- basements and semi-basements of high-rise buildings.
The Town Planning Code formulates different types of capital repairs of housing. Comprehensive - represents the modernization of the entire system or its complete replacement. Partial restoration is the selective replacement of structural elements, parts or systems. The list of services and works performed can be supplemented with certain items; the issue is resolved at the level of regional authorities. Depending on the condition of the home, which is determined as a result of a technical inspection, the following may also be included:
- measures to improve energy efficiency in order to save energy resources in an apartment building: installation of control units and meters, replacement of stove heating with any other, insulation of external walls and facade;
- installation of ventilation equipment;
- a number of other necessary works.
Read also: How to write and submit a complaint to the housing inspection: sample and procedure for registration
After amendments to the legislation, home owners can finance any other services and work that are not on the approved list. To do this, it is necessary to conclude an agreement and increase the amount of cash payments to the building restoration fund. In some cases, residents can count on help from the state; under what conditions funds for the restoration of residential buildings are distributed among the constituent entities of the Federation is stated in Art. 17 of the law.
About the formation of the fund
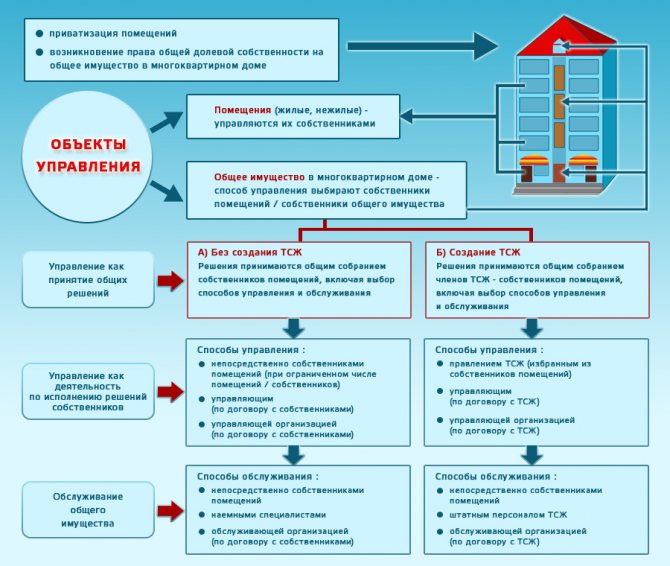
Many apartment owners began to think about creating an HOA and their own savings for major repairs. Compared to general regional operators, which receive funds from the majority of the population, there are several advantages of this form of home maintenance:
- the scheme for using funds is more transparent, residents of the house are given the opportunity to independently familiarize themselves with the reports in the fund for the period of interest in order to assess what the funds were used for;
- all decisions are made at a meeting of owners of common property, and the list of services, necessary work, their priority are determined by pressing problems and much more quickly than according to applications to the common fund;
- Responsibility for the implementation of measures and decisions is assigned to specific individuals, from whom, by concluding a preliminary agreement, a report on the work done can be demanded if the amount completed does not meet expectations.
These are the most obvious positive aspects; the disadvantages include the slow accumulation of funds in such a fund. It is almost impossible for residents to “patch up” an old high-rise building with a small number of apartments at their own expense - such buildings require too much work and materials.
How to regulate the process
For those wishing to form a HOA, the law on major repairs specifies methods for forming a fund and options for auditing documentation:
- reporting on the use of funds for the restoration of an apartment building is generated from January 1 to December 31 of the current year. The main final report is prepared no later than April;
- An annual report on the use of accumulated resources for capital repairs of apartment buildings should be considered a list of papers, which includes reports on the flow of funds transferred and credited to personal accounts, on the replenishment and investment of temporarily unused funds, and audit reports. The reliability of the data is confirmed by conducting an audit;
- services and works approved by law can be financed from a specific fund after consideration of the application for these works;
- all information about the activities of this non-profit financial organization, reporting for the past period, the results of audits and other checks are posted on the official website and must be publicly available.
There, co-owners of residential property can see the monthly calculation of tariffs, information about debts and penalties. An audit of an organization’s financial activities is carried out as follows:
- this is a mandatory procedure that is carried out annually based on the results of the fund’s activities;
- the board selects and approves an authorized audit company that carries out the audit;
- an extraordinary audit can be carried out at the initiative of the council at any time.
Thus, the functioning of such an organization is very clearly regulated. On the basis of Law No. 44, participation in tenders for major repairs of residential buildings is carried out. Legal companies and individuals who provide this type of service, the materials they supply must meet certain requirements and be within a certain price category. Otherwise, financing is carried out illegally and may be regarded as money laundering.